In the world of healthcare and diagnostics
Things are always changing. Recent technologies are constantly developed to help patients receive faster, more accurate diagnoses with less invasive procedures.
This article will discuss the role of Computerized Tomography (CT) and Computed Axial Tomography (CAT) scanning in healthcare. We’ll examine these terms, their use, and why they’re essential for diagnostic procedures. Furthermore, we’ll explore new advancements in CT and CAT scanning that have recently been implemented in hospitals around the country. These strategies are called Computerized Axial Tomography (CAT) scan and Intensity-Modulated CT (IMCT) scan, which are safer but more accurate than traditional methods.
What Is A CT Scan?
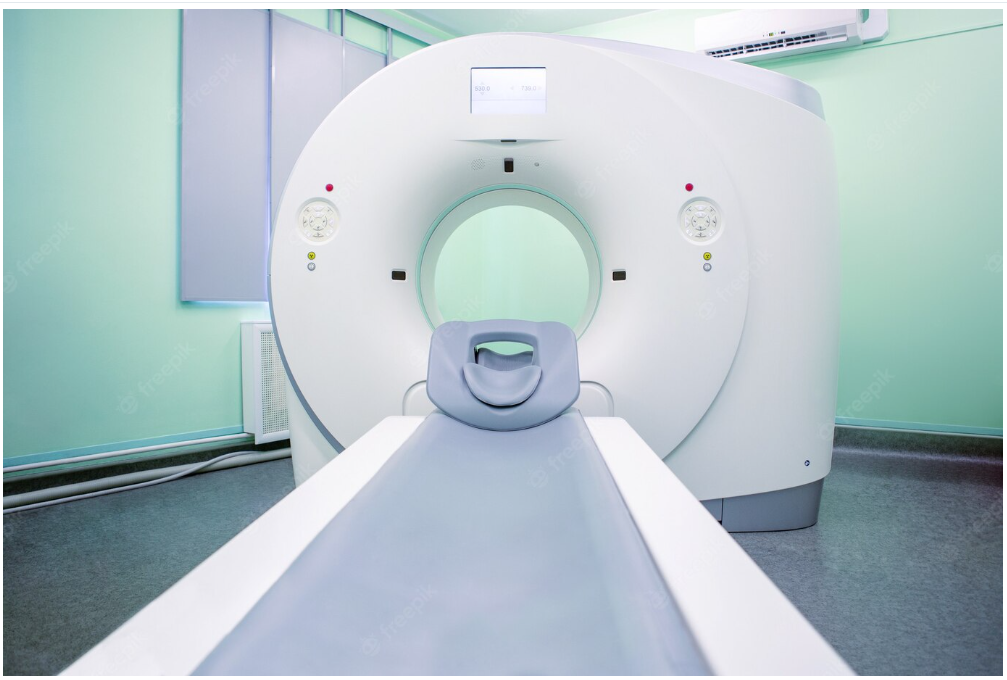
A CT scan is a technology that uses computerized X-rays to create 3D images of the inside of the human body. CT scans allow healthcare professionals to evaluate a patient’s internal organs, bones, and soft tissue to check for signs of illness or disease. The scan itself is relatively painless and non-invasive. You may be given an injection of a special dye before the scan to enhance the quality of the images.
Depending on the portion of the body you’re being scanned, the scan may take between 10 and 60 minutes. The whole process for a CT scan is as follows: A patient is placed on a table inside a large machine called a CT scanner, where they will remain still for the duration of the scan.
The table inside the scanner rotates around the patient’s body, moving them into different positions as the scanning process takes place. The scanner also moves around the patient, capturing several images as it does so. The patient’s body will be in a cradle within the machine. Several X-ray beams pass through the patient’s body. The beams are controlled by a computer, programmed with the body parts that should be examined.
The computer then uses the information collected by the X-rays to create 2D images of the body. These 2D images are then pieced together to create a 3D image of the body that doctors and other healthcare professionals can review. The CT scanner then spits out a CD of the photos, which can be uploaded to a computer to be examined further.
What Is A CAT Scan?
A computerized axial tomography (CAT) scan is a type of computerized tomography (CT) scan that can be used to obtain more detailed images of the brain or other parts of the body that are difficult to image with a standard CT scan.
It is called “computerized” because a computer is used to control the process and “axial” refers to the axis (or center) of the body. It is also called a “CT scan” because it uses X-rays the same way as a standard CT scan does. A computerized axial tomography scan (CAT scan) is an imaging test used to diagnose diseases or investigate brain, spine or blood vessel injuries.
During the diagnosis, you lie on a table that slides into a large doughnut-shaped machine. The table moves through the device while the machine makes a series of rotating X-rays that take pictures of your body. A computer puts the images together to develop a picture of the inside of your body. The checkup is painless and takes about 20 minutes to complete.
How Are CT And CAT Scans Used?
CT scans are often used to diagnose health issues or diseases. They can detect problems in the chest, abdomen, pelvis, or spine, as well as internal bleeding or blood clots. CT scans are also used to evaluate the effectiveness of medical treatments, such as chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and surgery.
CT scans are most often used on patients who have experienced trauma or have characteristics such as chest pain, the difficulty of breath, fever, or abdominal pain requiring a more thorough diagnosis.
A CAT scan is a special CT scan that can be used to look at tiny parts of the body, such as the brain and spine. This is particularly helpful for patients who have experienced head trauma or who have certain types of brain tumors.
Why Are These Advances Important?
CT and CAT scans have been used in hospitals for many years. They are an invaluable technology that has allowed doctors to make quick and accurate diagnoses in many different situations. However, until recently, CT and CAT scans had a few limitations.
Firstly, they required patients to be injected with a dye to enhance the contrast of the images. This dye carried some risks, as it could cause allergic reactions and be toxic if it got into the bloodstream. The second issue was that the scans produced large, high-resolution images that were difficult to interpret.
As a result, doctors had to spend time analyzing the photos, which delayed their ability to deliver accurate diagnoses. The advancements in CT and CAT scanning that have been implemented in most hospitals around the country address these issues. These new strategies are called Computerized Axial Tomography (CAT) scan and Intensity-Modulated CT (IMCT) scan.
Instead of the dye that was used in the past, the new imaging strategies use an intravenous injection of harmless, inert gas. These gas particles are able to enhance the contrast of the images while also being undetectable by the human body. With these enhancements, the new CT and CAT scans are safer but more accurate than traditional methods.
Future Of CT And CAT Scans
It will save hospitals money, reducing the need to upgrade and retrofit their scanning machines. Additionally, using gas particles is safer, as it does not require patients to be injected with a dye that could result in allergic reactions or be toxic if it gets into the bloodstream.
The second advancement is that the new imaging strategies produce much lower resolution images that are more easily interpreted. As a result, it will allow doctors to make diagnoses much more quickly, benefiting patients.
Conclusion
CT and CAT scans have become an indispensable part of modern healthcare. The CT scan has allowed doctors to detect signs of illness or disease in the body that the patient could not observe or feel. The CT scan has also been used to evaluate the effectiveness of medical treatments, such as chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and surgery.
New advancements in CT and CAT scanning will hopefully be able to address the critical shortcomings of the current technologies. Firstly, the use of gas particles in the new imaging strategies is more accurate and requires less modification of the technologies.