Medical imaging has dramatically changed diagnosis, monitoring, and treatments of diseases. Among such innovative technologies, PET CT scans an integration of Positron Emission Tomography (PET) and Computed Tomography (CT) that depends on the impact of radioactive tracers for full comprehension of how the body functions. This non-invasive tool has become instrumental in diagnostics, particularly in oncology, neurology, and cardiology. With advanced PET CT services now available in diagnostic labs across Bengaluru, such as Kiran PET CT, we see how radioactive tracers are transforming the future of medical imaging.
What Are Radioactive Tracers?

A radioactive tracer or a radiotracer is a chemical compound used in trace amounts, which is tagged with some miniature amount of radioactive material. The tracers are produced with an intention of mimicking a physiologic compound inside the body, meaning that they remain with physiological processes such as metabolism, blood flow, or cell growth. Infused inside the human body, the released positrons from the tracers inside are detected by the PET scanners and form detailed images on how tissues and organs function at the molecular level in real time.
Unlike most other diagnostic imaging methods that can outline anatomical structures only, such as bones, organs, or tumors, PET scans based on radioactive tracers produce functional images. Being able to image not only the structure itself but also processes in the body has made PET CT scanning irreplaceable in modern diagnostics.
How PET CT Scans Work
A PET CT scan is a combination of two single scan techniques:
Positron Emission Tomography (PET): This imaging method injects radioactive tracers into a patient’s blood flow in order to focus on cellular activity. Since cells throughout the body absorb the tracer, areas with higher metabolic activity, such as cancer cells, will be brighter, and the disease will be recognized.
Computed Tomography (CT): CT scans provide clear, detailed images of the internal body structures through X-ray. The structural information, thus acquired, makes it easier for radiologists to identify precisely where in the body abnormal conditions lie.
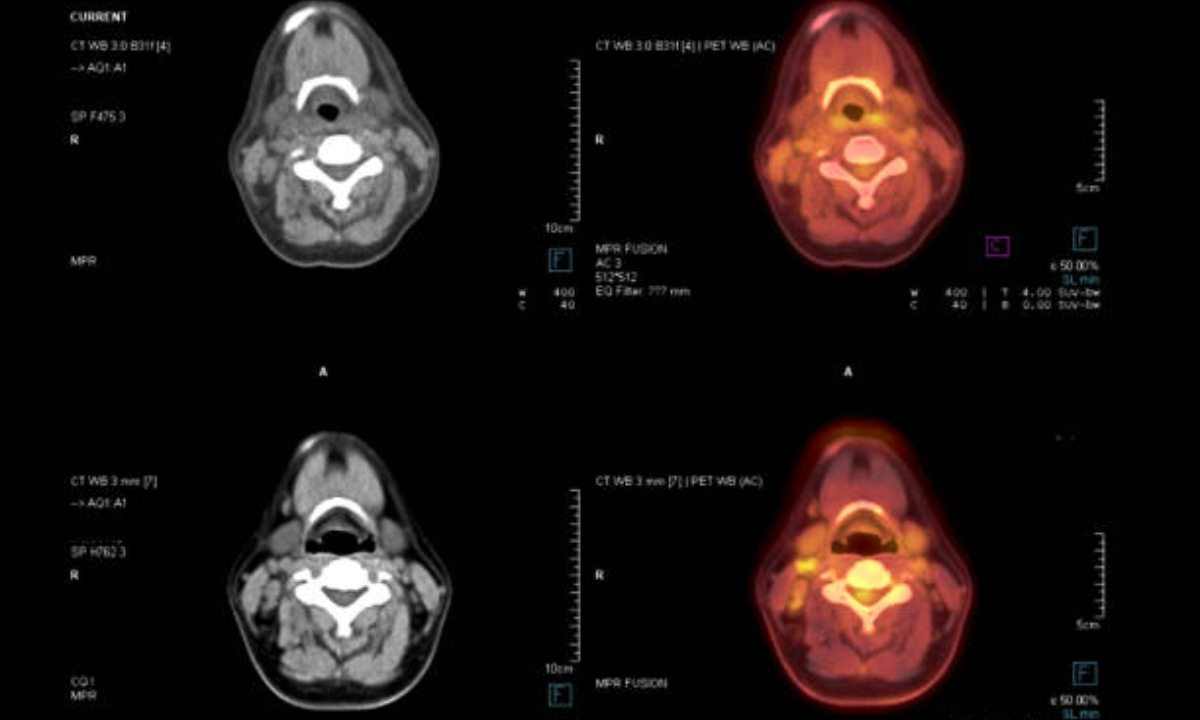
Combining PET and CT images can elucidate diseases such as cancer, Alzheimer’s, and cardiovascular conditions in better detail regarding location and activity.
Role of Radioactive Tracers in PET CT Scans
PET CT scan mainly depend on radioactive tracers used. Among many radiotracers, Fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) is the most commonly used radiotracer in PET imaging, which is a radioactive glucose molecule. Because cancer cells consume glucose at much higher rates than normal cells, FDG helps the PET scanner to highlight the area where the rate of glucose uptake is high, thus doctors can detect the cancer tumors or monitor the outcome of treatment.
Other radiotracers may be employed for other types of diagnostics:
Oxygen-15 and Nitrogen-13: The two are used in the examination of the utilization of oxygen and bloodstream, primarily in heart or brain scans.
Carbon-11 and Fluorine-18: These are employed in brain imaging in an attempt to diagnose conditions such as epilepsy or dementia.
Gallium-68: This is utilized in the diagnosis of neuroendocrine tumors.
The tracer is introduced to the patient. It follows the bloodstream circulation course and circulates to places in the body where the biological activity is high. This radioactive tracer decays and captures the gamma rays by the PET scanner that gives a detailed picture of biochemical activity in the body. Simultaneously acquired CT scan has been shown to give a more detailed structural image of bones, organs, and tissues. The hybrid diagnostic tool that may sometimes allow detecting the earliest signs of disease, even before symptoms arise, is produced by combining PET and CT scans.
Advantages of PET CT Scans in Diagnosis
1. Early Detection of Diseases
Probably the greatest advantage of PET CT scans is the detection of diseases at their early stages. For instance, in oncology, it can even determine some growths which relate to cancer even before they appear in other conventional tests on imaging. Early detection means that the patient is treated earlier, and the chances of recovery are much enhanced.
2. Accuracy in Treatment Planning
PET CT is sometimes used for cancer staging, or the evaluation of the spread of the malignancy in the body. This level of detail helps the oncologists to alter their treatment based on the needs of the patient. Moreover, it also presents the progress of a patient about chemotherapy or radiation. Here, depending on the scan comparison before and after these treatments, it’s diagnosed that a tumor has reduced or remained the same.
3. Non-invasive and Safe
PET CT scans with radioactive tracers are absolutely safe and non-invasive. The concentration of radioactive substances is minimal, and thus, they decay rapidly to minimize exposure to radiation. The patient will not undergo surgical procedures for the sake of guaranteeing a comfortable stress-free experience.
4. Wide Range of Applications
Besides oncology, PET CT scans have such a great worth in diagnosis and management of neurological and cardiovascular diseases. Neurologically, PET CT can pick early signs of Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s, or epilepsy by looking at metabolic activity in the brain. Cardiologically, PET CT scans can show areas of the heart not being perfused appropriately. The findings thus guide the doctors to diagnose coronary artery disease or in patients planning an intervention, either surgery or angioplasty.
Conclusion
Radioactive tracers play a crucial role in medical imaging, providing accurate and detailed insights into various conditions, from diagnosing organ function to detecting cancer. This proven, minimally invasive method is safe, reliable, and conducted under the supervision of certified medical professionals. Any side effects are usually mild and temporary. If you have concerns about your medical imaging needs, such as PET or CT scans, you can reach out to Kiran PET CT for expert assistance.