Introduction
Fibroblast activation protein (FAP) is a protein that is overexpressed in the tumour microenvironment of various types of cancers, including breast, lung, pancreatic, colorectal, and more.
What does a FAPI PET/CT scan do?
PET/CT technology combines the functional information from positron emission tomography (PET), which detects the distribution of the radioactive tracer, with the anatomical information from computed tomography (CT), which provides detailed images of the body’s internal structures. This hybrid imaging approach helps in cancer imaging by localising and characterising tumours more accurately.
Understanding FAPI PET-CT Scans
FAPI (Fibroblast Activation Protein Inhibitor) and its significance in cancer imaging
- High sensitivity and resolution- 68-Ga-FAPI PET/CT offers high sensitivity. This enables the detection of small tumours or metastases, which otherwise might be challenging to identify using other imaging techniques.
- Staging and restaging- 68-Ga-FAPI PET/CT is valuable for staging cancer. It helps to determine the extent to which the disease has spread in the body. It is also useful in monitoring the response to treatment and restaging patients to assess treatment efficacy.
- Personalised treatment- The information obtained from 68-Ga-FAPI PET/CT can aid in guiding treatment decisions and planning. This can potentially lead to more personalised and dedicated forms of therapy.
- Minimal radiation exposure- : Gallium-68 has a short half-life (about 68 minutes), which means that patients are exposed to a relatively low amount of radiation during the imaging procedure. This makes it safe for use in clinical settings.
- Safety and tolerability- The general conclusion from research has shown that Gallium-68 FAPI PET/CT is safe and well-tolerated in patients.
- Emerging research- 68-Ga-FAPI PET/CT is an area of active research and is not yet available everywhere. However, its potential in oncology and early cancer diagnosis has shown promising results in preclinical and early clinical studies.
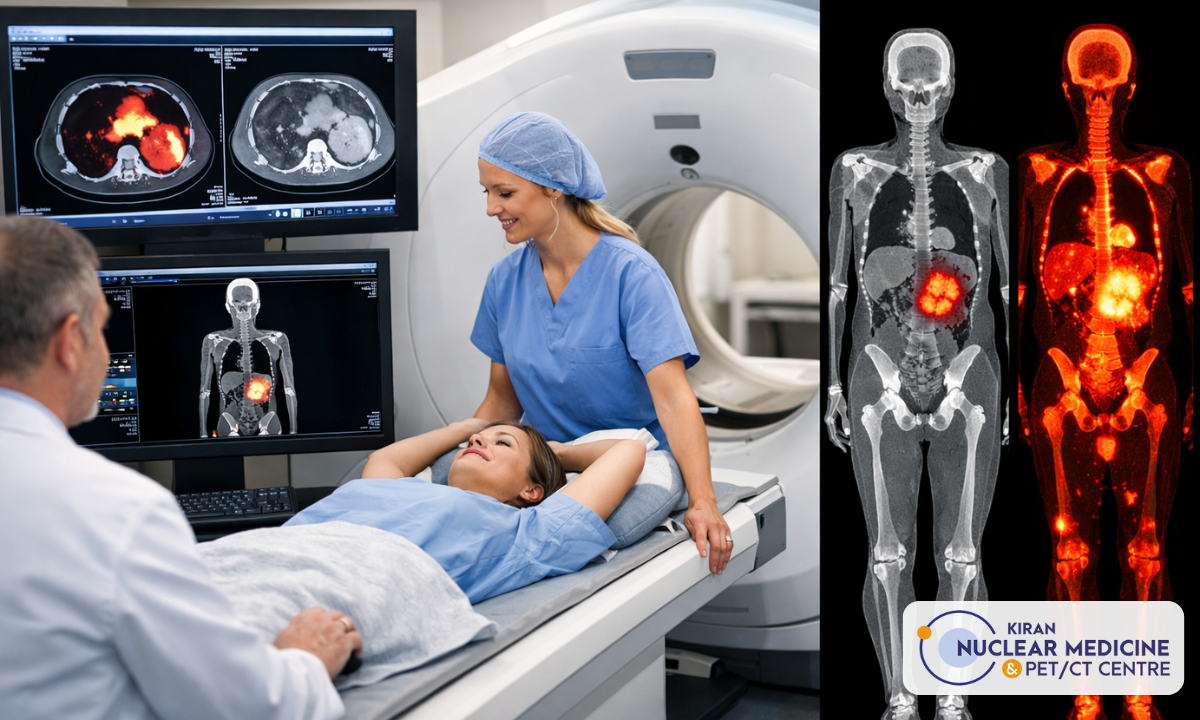
PET-CT scans and how they work in cancer detection
A PET or positron emission tomography scan is an imaging test that can help to reveal the metabolic or biochemical function of an individual’s tissues and organs. The PET scan uses a radioactive drug called a tracer to show both typical and atypical metabolic activity. A PET scan can often detect the atypical metabolism of the tracer in diseases before the disease shows up and can be identified on other imaging tests, such as computerised tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). The tracer is most often injected into a vein within the person’s hand or arm. The tracer will then collect into areas of their body that have higher levels of metabolic or biochemical activity. This often pinpoints the location of the disease. The PET images are typically combined with CT or MRI and are together called PET-CT or PET-MRI scans.
Applications of FAPI PET-CT scans
According to research and clinical studies, the following types of cancers are reported to be potentially detectable using Gallium FAPI PET/CT:
- Pancreatic cancer
- Colorectal cancer
- Breast cancer
- Lung cancer
- Ovarian cancer
- Gastric cancer
- Prostate cancer
- Head and neck cancers
- Soft tissue sarcomas
- Some types of skin cancers
A non-invasive scan with minimal side effects
Coming as a sigh of relief to people who are afraid of any medical examinations and techniques, one of the most remarkable characteristics of FAPI PET-CT scans is their non-invasive nature. Unlike many other diagnostic procedures, these scans do not require any incisions, needles, or uncomfortable instruments. Instead, patients simply need to lie comfortably on the scanning table while the equipment does its work. This non-invasiveness ensures that patients experience minimal discomfort during the procedure.
Furthermore, these scans come with absolutely minimal side effects. Most patients report feeling no or very mild side effects, such as temporary dizziness or a metallic taste. These side effects typically fade quickly, and patients can resume their daily activities in their day-to-day lifestyles shortly after the scan. This convenience and minimal disruption to one’s routine make FAPI PET-CT scans a patient-friendly choice for cancer diagnosis and monitoring.
Analysing a FAPI PET-CT Scan- What does it tell doctors?
The analysis and interpretation of FAPI PET-CT scan results requires the knowledge and expertise of healthcare professionals, typically radiologists and oncologists. They carefully scrutinise the images generated during the scan to make accurate assessments.
- Image Review: Radiologists examine the detailed images from the results, looking for areas of increased or abnormal tracer uptake. These areas often indicate cancerous tissue. Next, the extent and location of the cancerous tissue are assessed.
- Comparative Analysis: The radiologist may also compare the FAPI PET-CT results with results of previous scans, if available, to track any changes over time, such as tumour growth or shrinkage during treatment.
- Quantitative Data: Special technical software is used to measure the level of tracer uptake quantitatively. This helps professionals to understand the intensity of the abnormalities.
- Clinical Context: The interpretation doesn’t happen in isolation. The patient’s clinical history, their symptoms, and other diagnostic tests are considered, so as to produce a comprehensive diagnosis or treatment plan.
- Collaboration: Oncologists often collaborate with radiologists to ensure that they take a holistic approach to the care and treatment of the patient, based on the scan results. Their combined professional expertise is crucial in making informed decisions regarding cancer diagnosis, staging, and treatment.
Conclusion
The benefits and key points of FAPI PET-CT scans are many, and briefly summarised, include
- Early Detection: These scans are excellent at detecting even small cancerous lesions, enabling early diagnosis.
- Precision Imaging: The scans create detailed maps of cancer in the body, thus enhancing doctors’ understanding and planning of treatment.
- Treatment Monitoring: The technology behind these scans help track the effectiveness of cancer treatments, allowing adjustments as needed.
- Non-Invasive: The procedure is non-invasive and does not involve any incisions, making it patient-friendly.
- Minimal Side Effects: Patients typically experience only minimal side effects which are short-lived. Side effects may include mild dizziness or a metallic taste.
- Expert Analysis: Radiologists and oncologists analyse scan results, ensuring accuracy and informed decision-making.
- Future Promise: Ongoing research promises further advancements in cancer diagnosis and treatment using FAPI PET-CT scans.
In conclusion, FAPI PET-CT scans are a powerful and non-invasive tool for cancer diagnosis and imaging that offer early, precise, and personalised care for cancer patients, with minimal discomfort and promising future developments.
It is of utmost importance to take care of one’s health. When going for medical procedures such as PET-CT scans, it is advisable to get them done in places with state of the art medical equipment with well qualified professionals. Kiran PET-CT Diagnostic Centre is one such place at Indiranagar, Bangalore, where you will get access to the best quality PET-CT diagnosis, including FAPI PET-CT scan.