HNCs are a type of cancer that grows very rapidly, and they form a huge share of the overall health burden in India because they hold the highest cases globally. The carcinoma mostly arises within the squamous cells of the mucosal epithelial lining and spreads to any and every region anatomically located there, like within the oral cavity, throat, nasal passage, and salivary glands.
HNC is a significant challenge, especially with late diagnosis, and poor awareness, and tobacco accounts for 80-90% of oral malignancies in India. Early detection and accurate staging increase the possibility of better outcomes and new imaging techniques, including Gallium-68 fibroblast activation protein inhibitor 68Ga-FAPI PET/CT, may hold promise for resolving some of these challenges.
Symptoms of Head and Neck Cancers
HNC may present with varied symptoms according to the site and stage of the tumor:
- Recurring swelling or lumps.
- Pain or difficulty in swallowing.
- Voice changes or hoarseness.
- Chronic sore throat or ear pain.
- Unintended weight loss.
- Difficulty in breathing.
- Bleeding or numbness in the affected area.
Epidemiology in India
India is expected to see a 57.5% rise in cancer cases by 2040, with head and neck cancers largely being responsible for this trend. The reasons can be high prevalence tied to tobacco use, along with lack of access to proper healthcare at the right time, which makes most patients come in at advanced stages. Detecting head and neck cancer with a PET scan can help in accurate diagnosis and treatment.
Types of Head and Neck Cancer
- Pharyngeal Cancer: This type is found in the upper windpipe or larynx and affects respiration, speech, and deglutition.
- Nasopharyngeal Cancer: Arises in the nasopharynx, which is the upper throat behind the nose.
- Hypopharyngeal Cancer: Found in the hypopharynx, around the larynx.
- Nasal Cavity and Sinus Cancer: Occurs in the spaces behind the nose.
- Salivary Gland Cancer: Occurs in glands that make saliva, which aids in digestion.
- Oral Cavity Cancer: Includes cancers of the lips, mouth, tongue, gums, and the roof of the mouth.
- Oropharyngeal Cancer: It comprises the base of the tongue, tonsils, and posterior pharynx. A major cause includes HPV and tobacco and alcohol consumption.
- Tonsil Cancer: It constitutes about 3.5% of oral cancers and is largely a secondary consequence of tobacco and HPV.
Limitations of Anatomical Imaging in HNC
The anatomical imaging modalities that have transformed the diagnosis and staging of HNC include CT, MRI, and 18F-FDG PET/CT. However, they have the following limitations:
- High nonspecific uptake of 18F-FDG in normal tissues and inflammation leads to false positives.
- Low FDG avidity is another reason for false negatives, such as small primary tumors in the oropharynx.
- Preparation of Patients: Fasting and strict glucose level control are required before imaging with 18F-FDG, making it a cumbersome procedure.
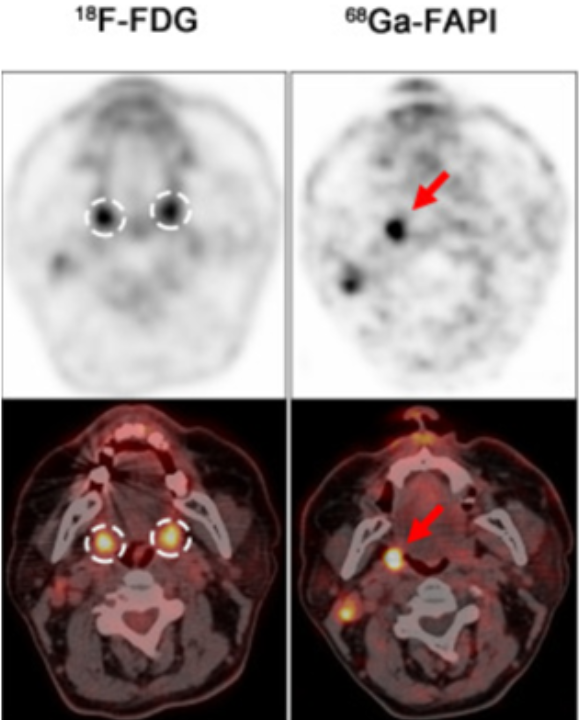
Role of 68Ga-FAPI PET/CT in HNC
Overexpressed in CAFs, fibroblast activation protein (FAP) is a cell type widely spread within the stroma of epithelial carcinomas. 68Ga-FAPI PET/CT exploits this to have better diagnostic accuracy and a significantly higher TBR as compared to 18F-FDG PET/CT.
Advantages of 68Ga-FAPI PET/CT
Better diagnostic accuracy:
The sensitivity, specificity, and positive predictive value have been significantly enhanced in the diagnosis of primary tumors with 68Ga-FAPI PET/CT.
Higher TBR:
Higher TBR offers the superior differentiation of malignant from normal tissues, particularly in high nonspecific uptake areas, thus placing FAPI PET/CT on a higher pedestal.
Detection of Small and Latent Tumors
Small, mucinous, and adenoid carcinomas are easily detected using FAPI PET/CT, but they can be evaded by FDG PET/CT.
Use of 68Ga-FAPI PET/CT in Head and Neck Cancer
1. Diagnosis of Primary Tumors
Several studies have developed the following results of 68Ga-FAPI PET/CT:
- Increased avidity was observed in malignant primary tumors of the Waldeyer tonsillar ring
- Tumor detection in the oropharynx is found to be better sensitivity than FDG PET/CT with highly significant uptake
- It determines the primary tumors in cases of unknown origin, thus reducing diagnostic doubt
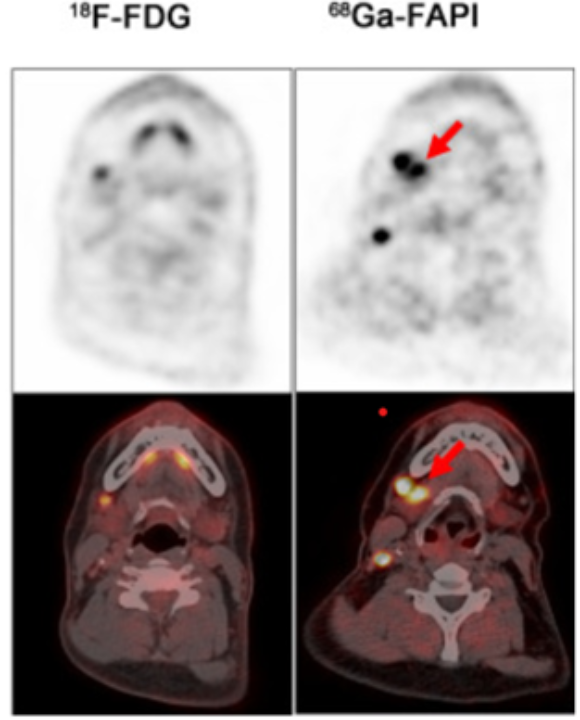
2. Evaluation of Metastatic Disease
Lymph Node Metastases: It is relatively more sensitive than FDG PET/CT. FAPI PET/CT has a higher TLR for the assessment of lymph nodes.
Bone Metastases: It provides more diagnostic sensitivity with no noise background. It gets images less distorted.
3. Recurrence Detection
68Ga-FAPI PET/CT is used in recurrent HNC and detects significantly more. Tumor recurrence, especially in patients with the oral cavity, nasopharynx, and salivary gland cancers where lesions may also be mucosal or submucosal.
Comparison 68Ga-FAPI vs 18F-FDG
68Ga-FAPI PET/CT has higher sensitivity, positive predictive value, and accuracy in locating the primary tumors in head and neck cancers of unknown primary patients.
FAPI PET/CT is superior in detecting primary tumors of HNC of unknown origin and thus confers a critical advantage in challenging situations.
Potential Limitations of FAPI PET/CT
Although 68Ga-FAPI PET/CT has shown tremendous promise, there are still some challenges:
Physiologic Uptake: Conditions like arthritis, periodontitis, and wound healing can cause false positives from fibrotic activity.
Cost and Availability: Not easily accessible in some geographical locations may limit it from being as widely adopted.
Conclusion
Imaging and the treatment of head and neck cancer will come from 68Ga-FAPI PET/CT, which would result in a small, well-hidden, or even non-FDG-avid tumor being detected better with more precision than by using classical methods.
The diagnostic scenario of HNC using the PET scan in the current scenario will be revolutionized through FAPI PET/CT as it will advance the detection of primary tumors, metastatic spread assessment, and localization of recurrent disease. In this respect, making this method more accessible and thereby cost-effective for more patients will be a challenge in itself.
Advanced imaging modalities like 68Ga-FAPI PET/CT are revolutionizing the present scenario in a country like India, where HNC is such a big burden, to achieve earlier diagnoses, more precise staging, and better patient outcomes in this challenging disease.