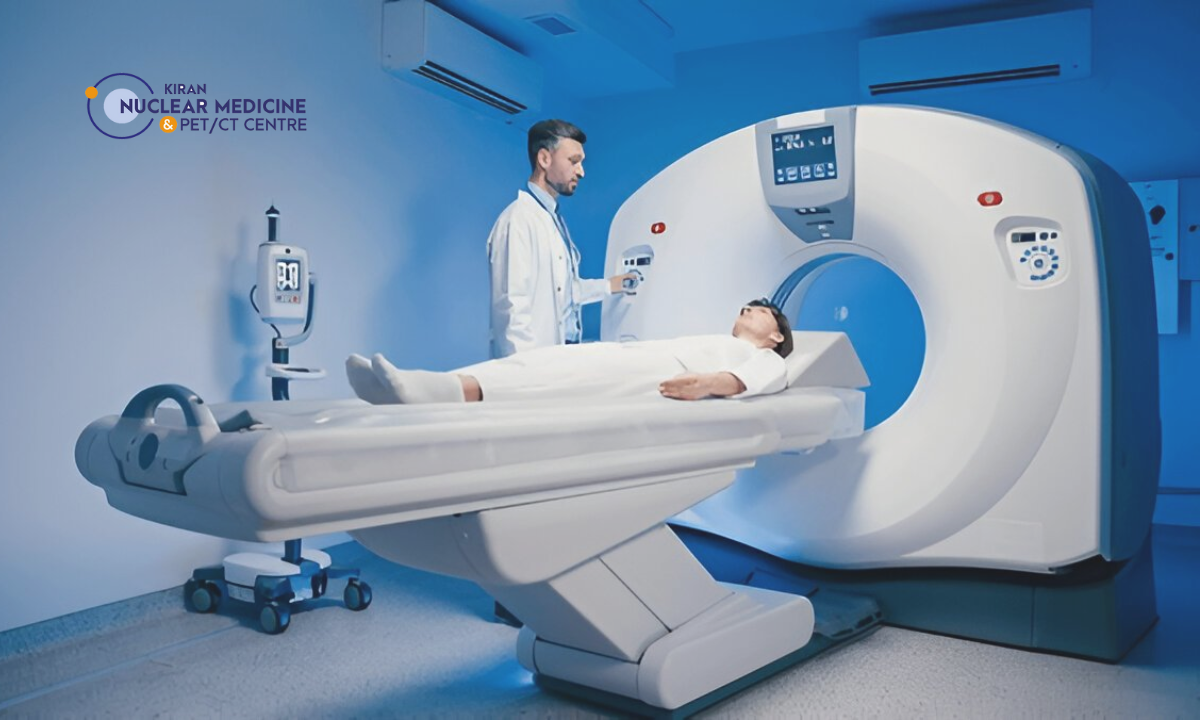
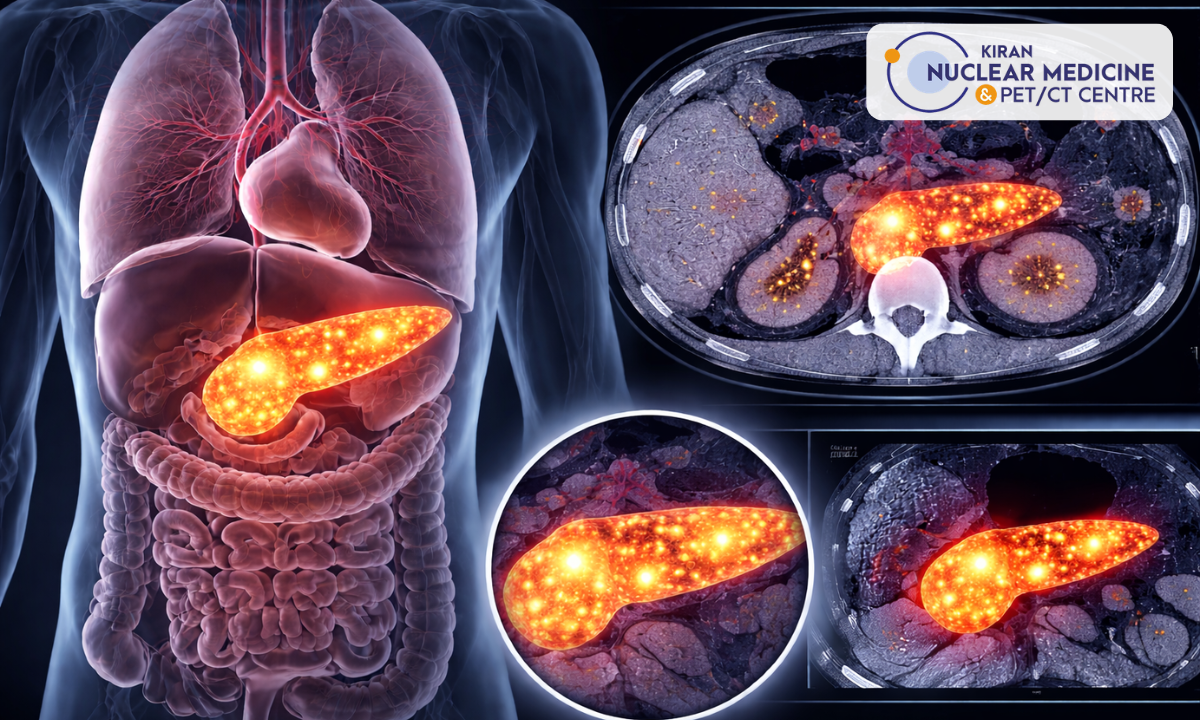
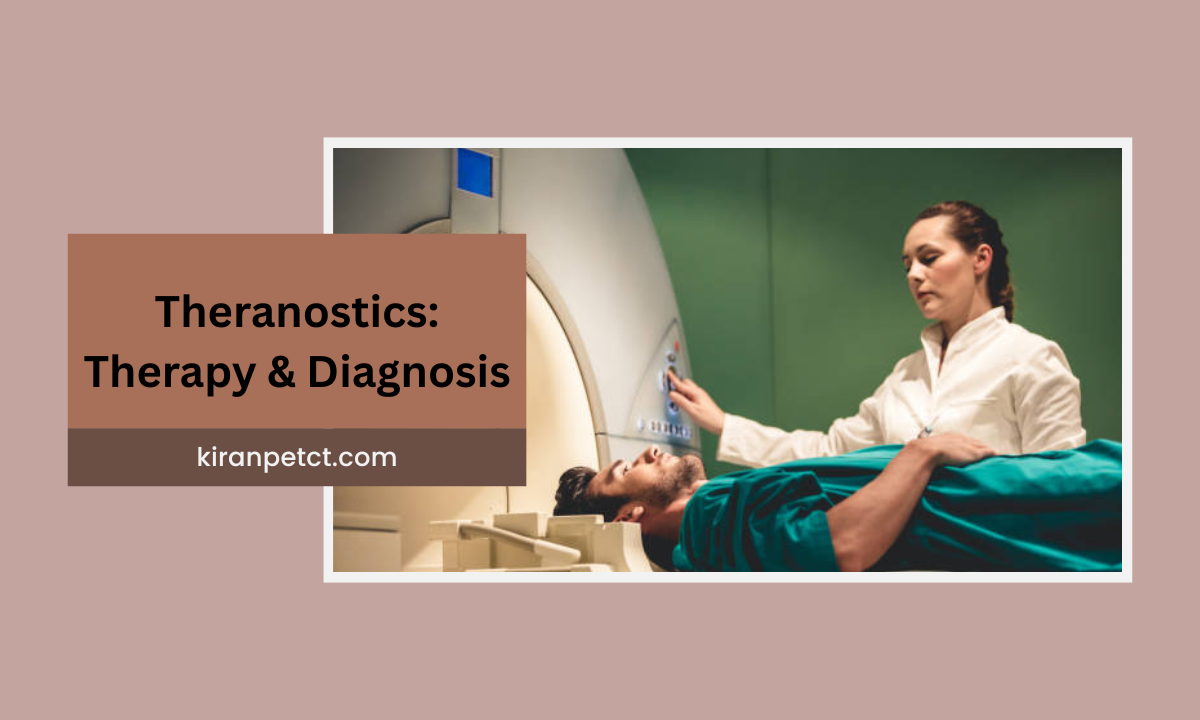
When I first walked into our imaging suite here in Kiran PET/CT, I realized that nuclear medicine technology is far more than just another diagnostic tool; it’s a blend of science, care, and precision that’s reshaping how we detect and treat some of the most serious diseases.
In my role at the centre, I see how nuclear medicine opens doors to answers where traditional imaging falls short, and I believe understanding its meaning, applications, and benefits will help you appreciate why it’s such a game-changer.
What Nuclear Medicine Means
At its core, nuclear medicine refers to a medical specialty that uses small amounts of radioactive substances (also called radiopharmaceuticals or tracers) to visualize how organs and tissues in the body are functioning. Unlike an X-ray or CT scan, which typically shows anatomy (what things look like), nuclear medicine lets us assess physiology (how things are working). The tracer is given by injection, inhalation or orally; it travels through the body and emits radiation detected by specialized cameras.
In plain terms, “nuclear medicine” is the use of radioactive agents to see inside the living body, not just in structure but in action.
How Nuclear Medicine Imaging Works
The process begins with a radiopharmaceutical, carefully chosen to target a specific organ or process (for example, the thyroid, heart muscle, or a tumor). Once administered, it accumulates in the relevant area. Imaging modalities such as PET (Positron Emission Tomography) or SPECT scan (Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography) then detect the radiation and produce images.
These images can reveal “hot spots” (where tracer uptake is unusually high) or “cold spots” (where uptake is low), which often correspond to disease activity, abnormal metabolism, or functional deficits. Some common scan types include bone scan, thyroid scan, cardiac perfusion scan, and whole-body PET/CT for cancer assessment.
Types of Nuclear Medicine Scans
I often describe this to patients in Kiran PET/CT like this: imagine your body’s engine has many parts, and some parts don’t just look different—they work differently. These scan types help us find those working parts. Typical nuclear medicine scan types include:
- Bone scintigraphy: to look for bone diseases, fractures, or metastases.
- Thyroid scans: to assess thyroid function or nodules.
- Cardiac perfusion scans: to assess blood flow and viability of the heart muscle.
- Whole-body PET/CT: especially in oncologic settings to detect cancer spread or monitor treatment.
- Hybrid imaging (e.g., PET/CT), which combines functional and anatomical data for better accuracy.
What Is Nuclear Medicine Therapy (and Advanced Theranostics)
While a major part of this field is imaging, one of the most exciting developments I have witnessed is nuclear medicine therapy. In many cases, we don’t just ‘see’ disease, we ‘treat’ it with targeted radiopharmaceuticals: a perfect blend of diagnosis and therapy known as Advanced Theranostics Therapy.
For instance, patients with certain cancers or thyroid disorders receive a radiopharmaceutical designed to lodge in the abnormal tissue and deliver radiation from within—destroying disease cells while sparing healthy tissue.
Nuclear Medicine for Cancer – A Vital Role
In our centre at Kiran PET/CT, many of the referrals I handle are for nuclear medicine for cancer, whether for staging, therapy planning or monitoring therapy response. Since cancerous cells often consume more glucose (in many cases) or have different uptake patterns, a PET scan can reveal areas of activity that other imaging might miss.
By identifying disease spread early (sometimes before symptoms appear), we can tailor treatments more effectively, and that often improves outcomes.
Key Benefits of Nuclear Medicine Technology
Working each day with these tools has convinced me of several major benefits of nuclear medicine technology:
- Early disease detection: Because functional changes often precede structural ones, we can detect abnormalities earlier than some other imaging methods.
- Functional insight, not just anatomy: We see how organs are working (or failing), not just what they look like. That gives us richer information.
- Less invasive, often safer: Many procedures only require the injection of a tracer; no major surgery for imaging.
- Targeted therapy with fewer side effects: In therapeutic use, radiopharmaceuticals can target disease cells with minimal impact on healthy tissue.
- Precision in treatment planning: For cancer and other serious diseases, nuclear medicine helps guide surgical decisions and radiation therapy and monitor response.
- Broad range of applications: from heart disease to brain disorders, bones to cancer, the scope is vast.
Why It Matters Here in Kiran PET/CT
Living and working in Kiran PET/CT, I watch how patients arrive worried, unsure why their symptoms persist or what hidden issue might be at work. With nuclear medicine technology available locally, we’re able to give them clarity. We’re not just imagining; they’re getting insight into how their body is functioning, enabling earlier and more accurate interventions.
And when I tell them about advanced imaging and therapies, like a PET scan in Bangalore (our region) or a targeted radionuclide therapy, they realize that even in our locality, global-level care is accessible. For many families, this means fewer trips, shorter wait times, and quicker decisions.
Addressing Safety and Myths
It’s natural to worry about radiation. I always pause to explain: the doses we use in nuclear medicine are carefully calculated, they are small and justified because the benefit (detecting or treating disease) outweighs the risk. We also follow strict procedures to protect staff, patients and the environment. Yes, there are limitations: some scans may take longer, or image resolution may not match CT in all cases, but overall, the functional data we obtain is incredibly valuable.
What’s Ahead—The Future of Nuclear Medicine
Looking ahead, I’m excited about how advanced theranostics therapy is transforming our field. New isotopes (for example, lutetium-177 and terbium-161) are opening possibilities for more cancers, for smaller metastases, and for combining diagnosis and therapy in one powerful step.
As technology evolves, we’ll see faster scanners, more precise tracers, better hybrid imaging (PET/CT, PET/MR), and, importantly, therapies that personalize treatment like never before.
Final Thoughts
In my daily work at Kiran PET/CT, I’ve come to believe that nuclear medicine technology is one of the most important advances in healthcare, because it doesn’t just show us “what’s wrong” but helps us understand “how it’s wrong” and even “how to fix it.” From imaging to therapy, from diagnosing early cancer spread to enabling targeted treatments, the role of nuclear medicine continues to expand.
If you or your loved ones ever face a diagnostic dilemma or a complex disease challenge, remember that with nuclear medicine, you have more than an image; you have insight. And with insight comes better decisions, better treatment, and greater hope.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: What exactly does nuclear medicine technology involve?
It involves administering a radiopharmaceutical tracer into the body, detecting the radiation it emits via specialized cameras, and creating images or delivering therapy based on that data.
Q2: How is nuclear medicine imaging different from a CT scan or MRI?
CT and MRI focus on structure, body parts, and how they look. Nuclear medicine imaging focuses on function, how organs or tissues are working, which often reveals issues earlier.
Q3: Is a PET scan in Bangalore the same as nuclear medicine?
Yes, a PET scan is a type of nuclear medicine imaging. If you’re in or near Bangalore and your doctor recommends a PET scan, it’s part of the nuclear medicine field.
Q4: What are the benefits of nuclear medicine for cancer patients?
For cancer, nuclear medicine helps with staging (knowing how far the disease has spread), selecting patients for specific therapies, monitoring response to treatment, and sometimes delivering the therapy itself in targeted form.
Q5: Is the radiation risk high in nuclear medicine scans?
No, the amount of radiation is quite low and has been used for decades under careful regulation. The benefit of accurate diagnosis or therapy typically outweighs the minimal risk.
Q6: What is Advanced Theranostics Therapy?
It refers to combining diagnosis and therapy in one approach—using radiopharmaceuticals that both detect and treat disease (for example, the same tracer targets a tumor, images it, and then delivers therapy).
Q7: If I’m in Kiran PET/CT, how can I access nuclear medicine services?
You can visit your local imaging or hospital centre offering nuclear medicine technology. They’ll guide you on the appropriate scan or therapy, explain preparations, and walk you through the next steps.