Cancer is one of the severe problems in medicine and its progression with the tumor microenvironment. In this dynamic ecosystem, cancer-associated fibroblasts play an important role in the growth of a tumor, metastasis, and therapeutic resistance. Recent advances in molecular imaging opened the door for the visualization and targeting of cancer-associated fibroblasts through the use of Gallium-68 fibroblast activation protein inhibitor PET/CT.
Knowledge of Tumor Microenvironment (TME)
The TME comprises the totality of cellular and non-cellular components that interact with cancer cells with the intent to modify their behavior and progression.
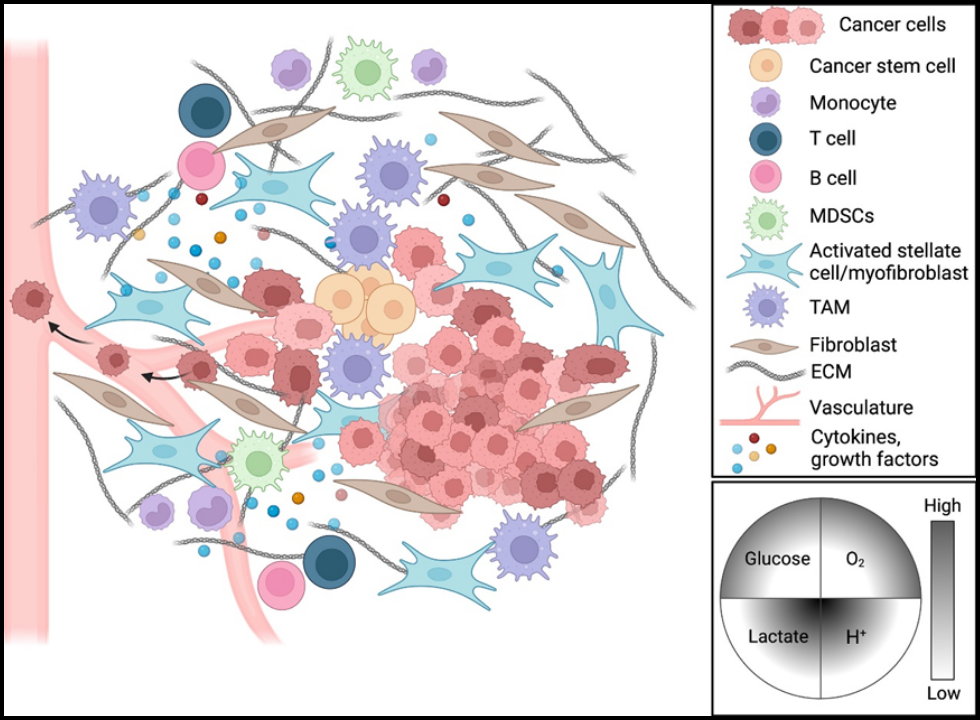
Stromal cell compositions can vary based on the type of tumor.
1. Non-Cellular Elements
ECM is one of the structural components of TME. This is a protein-proteoglycan composite network, offering support in the development and repair processes within tissues. In some way, tumors alter the organization of ECM and, consequently, enable the motion of cancer cells and their precursors, changing cellular signals or mechanical properties that promote growth and metastasis.
2. Cellular Components
Cancer cells recruit stromal cells from the adjacent tissues very vigorously for the development of the tumor stroma. These include:
- Fibroblasts
- Vascular endothelial cells
- Adipocytes
- Pericytes
Mesenchymal stromal cells derived from bone marrow
These stromal cells interact with cancer cells through mutual regulation that is the most prominent in the architecture, growth, metastasis, and drug resistance of the tumor.
Tumor Stromal Cell, the Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts: The Biggest Player in the Tumour Stromal Microenvironment
CAFs are a heterogeneous population of activated fibroblasts which form the main proportion of tumor stroma. These originate from more than one type of cells including fibroblasts, epithelial cells, endothelial cells, adipocytes, and pericytes. They operate through strong interaction with cancerous cells and other stromal components.
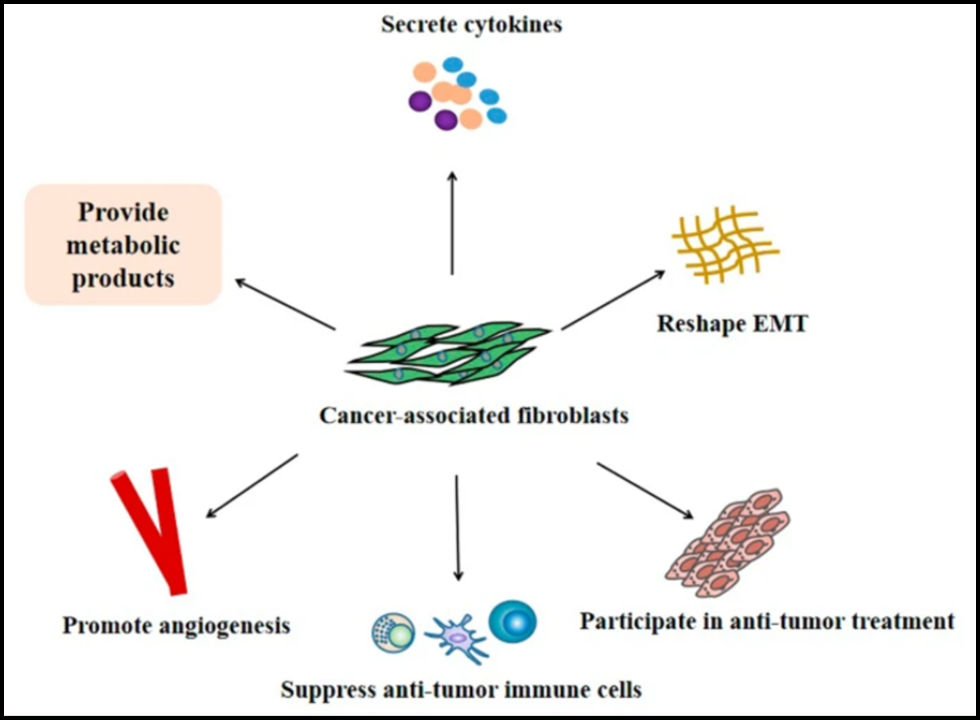
CAF can promote tumor growth by various mechanisms
How CAFs Support Cancer Progression
- Tumor Initiation: CAFs secrete factors that render the niche to become favorable to the cancer cells.
- Tumor progression: CAFs regulate the expression of growth factors, cytokines, and chemokines, all of which enhance tumor growth
- Metastasis: CAFs enhance the metastatic EMT which helps in the movement and invasion of cancer cells through the tissue and its colonization
- Therapeutic resistance: CAFs help in drug resistance by modifying TME, drugs get protected from the washout effect and immunosuppressive activity
This is an important milestone toward synthesizing radiolabeled FAP inhibitors in the treatment and diagnosis of cancer imaging.
What is FAPI PET CT?
Fibroblast activation protein inhibitor – FAPI PET/CT scan is one of the molecular imaging modalities newly developed for targeting FAP abundantly overexpressed on CAFs. FAPI strongly binds to the cell surface FAP and hence, both primary and metastatic lesions would be visualized in all body regions such as the brain, liver, pancreas, and gastrointestinal tract.
Benefits of FAPI PET CT
- High Sensitivity: It can detect very small-sized tumor lesions with high accuracy.
- Wide-range application: it can be applied for the imaging of different tumor types.
- Outstanding staging: its resolution is even better than that of conventional imaging techniques, contrast-enhanced CT, and MRI.
- Real-time visualization: more detailed information is provided concerning the biology of the tumor; in particular, the composition of the stroma.
Therapeutic Potential of FAPI
Besides diagnosis, FAPI has tremendous therapeutic potential. The two directions that are related to the agents like Gallium-68-imaging and Lutetium-177 for therapy are giving a glimpse into the ‘cure-all’ treatment of cancer.
Current Approaches Against Targeting CAFs
- Anti-differentiation to Tumor-promoting CAF: Interventions which inhibit the differentiation of stem cells into tumor-promoting CAF.
- Selective killing of Tumor-promoting CAF: This can be achieved through genetic approaches or antibodies that knock out the tumor-promoting CAFs, but there should be no loss of those CAFs that do not allow tumors to form
- Phenotypic Switching: Phenotypic switching of Tumor-promoting CAF into a more restrictive phenotype for the tumors
- Crosstalk Interference: Interference in the communication between CAF and Cancerous cells to suppress invasion, migration, and drug resistance of the tumors
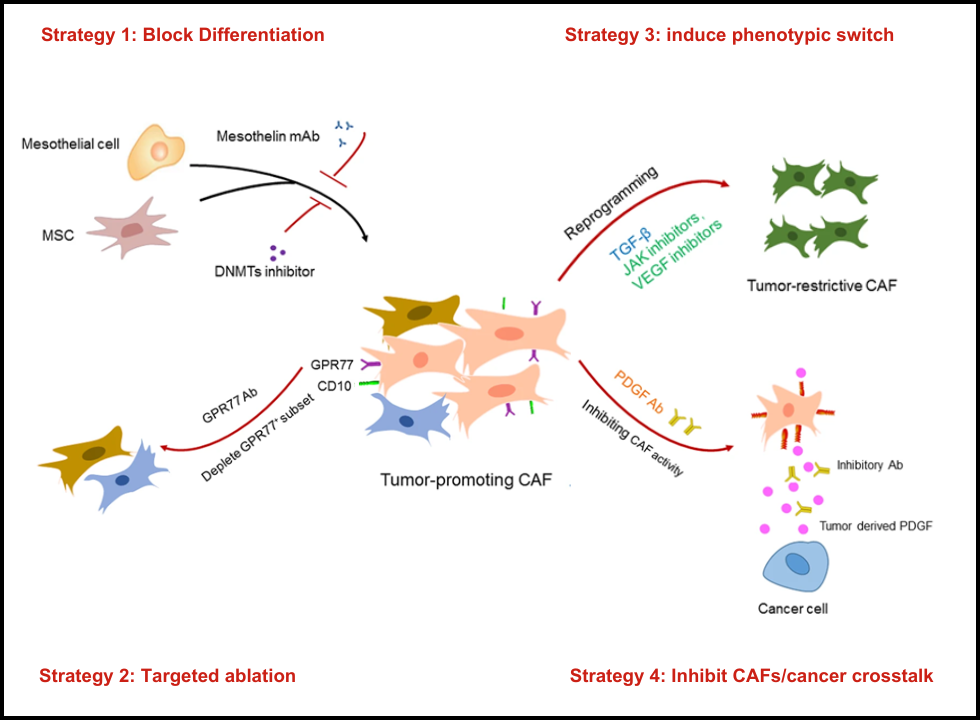
Selective targeting of Tumor promoting CAFs
Mechanism of FAPI treatment
This will use the specificity of CAFs for targeted treatment in the tumor microenvironment. For example, FAPI agents with Lutetium-177 will ensure that localized radiation therapy is performed without causing unnecessary damage to other healthy tissues.
Future of FAPI in Cancer Treatment
Indeed, FAPI PET/CT stands as one of the technologies revolutionizing oncology through an orientation that genuinely combines precision in imaging such as PET scan with an exact approach in therapy. The potential for patient outcome or quality of life is exponential. More integration with other forms of therapy, such as immunotherapy or chemotherapy, may explode further.
Conclusion
The next generation of diagnosis and treatment will be in the form of cancer diagnosis with therapy in conjunction with FAPI PET/CT targeting CAFs. The technology is, as a matter of fact, very well supported in such specificity towards the tumor microenvironment: an awareness of cancer intricacies.
With the development in radiochemistry and molecular biology science, FAPI agents will very soon be adopted in the personalized care of oncology. The brightest future of cancer management has never had a better leader. FAPI was more than a discovery; it confirmed that precision medicine could change many lives.