In the rapidly evolving field of healthcare, diagnostic technologies are continuously advancing, allowing healthcare providers to make quicker, more accurate diagnoses and thus improve patient outcomes. Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography scan commonly known as SPECT scan, combined with CT scanning, has revolutionized patient care. This hybrid imaging technique brings together the strengths of both SPECT, which uses gamma-ray-emitting radiotracers, and CT (Computed Tomography), which provides detailed anatomical images. The result is a powerful tool that enhances diagnostic accuracy and offers profound benefits in fields like oncology, cardiology, and neurology.
Introduction to SPECT/CT Technology

SPECT/CT is a dual-modality imaging method that integrates the molecular imaging capabilities of SPECT with the detailed anatomical mapping of CT scans. This innovative technology provides a three-dimensional view, which improves the localization of abnormal activity, ensuring clinicians have a comprehensive understanding of the area in question. Unlike traditional imaging methods that may lack specific functional insights, SPECT/CT helps detect early-stage diseases that might otherwise go unnoticed.
How SPECT/CT Works
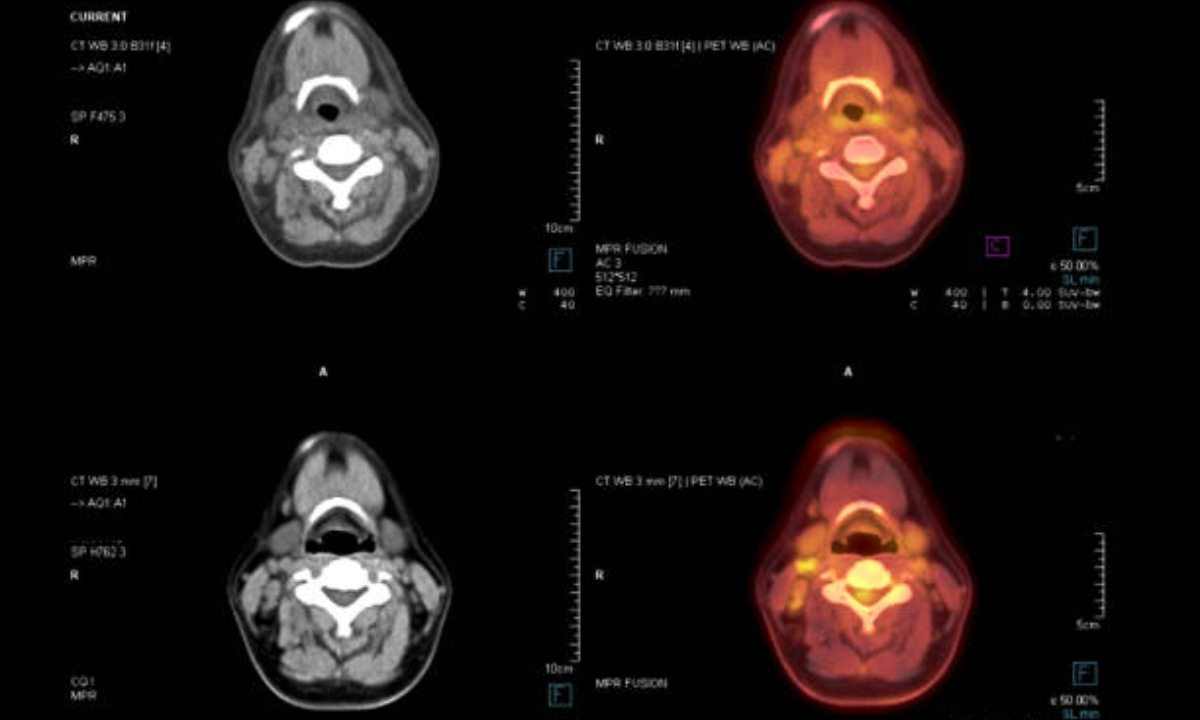
SPECT/CT imaging begins by injecting the patient with a radiotracer, a radioactive substance that travels through the bloodstream and targets specific areas of the body. As the radiotracer decays, it emits gamma rays, which the SPECT camera captures, providing images of the body’s internal structures and functions. The CT component captures high-resolution cross-sectional images, and these two datasets are merged to form a detailed, three-dimensional image. This fusion enables healthcare providers to accurately pinpoint abnormalities with greater precision.
The Clinical Applications of SPECT/CT
a. Oncology
SPECT/CT has significantly impacted oncology by improving cancer detection, staging, and treatment planning. It enables clinicians to distinguish between benign and malignant tumors and accurately assess cancer spread. This dual-modality imaging is especially useful in detecting bone metastasis, often difficult to identify with CT or SPECT alone. Moreover, SPECT/CT helps in monitoring the effectiveness of cancer treatments, allowing for adjustments that can increase the chances of successful outcomes.
b. Cardiology
Cardiology is another field that has benefited from the advent of SPECT/CT scans. By combining functional and anatomical imaging, this technique assists in detecting coronary artery disease, myocardial ischemia, and infarction. SPECT/CT scans provide valuable insights into the heart’s blood flow, offering a more accurate assessment of heart function and helping guide treatment decisions like angioplasty or bypass surgery. This imaging modality also plays a critical role in identifying patients at high risk for heart attacks.
c. Neurology
In neurology, SPECT/CT is instrumental in diagnosing and managing conditions such as Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, epilepsy, and other neurodegenerative disorders. SPECT/CT provides detailed images of cerebral blood flow and metabolism, offering insights into brain function that standard imaging cannot deliver. The technique helps identify areas with reduced brain activity and assists neurologists in understanding the extent and progression of neurological conditions.
Benefits of SPECT/CT in Diagnostic Imaging
a. Improved Diagnostic Accuracy
One of the primary advantages of SPECT/CT is its improved diagnostic accuracy. By merging functional and structural imaging, SPECT/CT minimizes ambiguities in the diagnostic process, reducing false-positive or false-negative results. Clinicians can confidently diagnose conditions that would be challenging to detect with traditional imaging.
b. Early Detection of Diseases
SPECT/CT scans enable the early detection of diseases, which can significantly impact patient outcomes. For example, in oncology, detecting cancer at an early stage increases the success rate of treatments. In cardiology, early diagnosis of heart conditions can prevent severe complications, while in neurology, early detection can lead to timely intervention, improving the quality of life for patients with degenerative brain conditions.
c. Reduced Need for Invasive Procedures
Because SPECT/CT provides detailed internal views without the need for invasive procedures, it reduces the need for biopsies and other surgical interventions. This non-invasive nature enhances patient comfort and safety, lowering the risk of complications associated with invasive diagnostic methods.
Limitations and Challenges of SPECT/CT
a. Radiation Exposure
One drawback of SPECT/CT is radiation exposure. While the amount is relatively low, repeated scans may increase a patient’s risk over time. Medical practitioners take every precaution to limit exposure, but this remains a consideration, especially for young patients and those who may require multiple scans.
b. Cost and Accessibility
SPECT/CT is an advanced and costly technology, and the high cost can limit access, particularly in regions with limited healthcare resources. Not all healthcare facilities have the infrastructure or funds to provide SPECT/CT, which can create disparities in patient care and diagnostic accuracy.
c. Requirement for Specialized Training
Using SPECT/CT effectively requires specialized training for radiologists and technicians. Proper interpretation of images necessitates a deep understanding of both functional and structural imaging, which may not be readily available in all healthcare settings.
Future Prospects of SPECT/CT
a. Technological Advancements
Technological advancements continue to drive the development of SPECT/CT, with innovations enhancing image quality and reducing scan times. Improved radiotracers are being developed to target a broader range of diseases, enabling even earlier detection and more specific imaging.
b. Potential in Personalized Medicine
SPECT/CT has significant potential in the field of personalized medicine. By tailoring treatments based on the functional and structural insights provided by SPECT/CT, healthcare providers can design personalized treatment plans that align with the unique needs of each patient. This approach enhances the effectiveness of treatments, reduces side effects, and improves overall patient outcomes.
c. Integration with Artificial Intelligence
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) with SPECT/CT is another promising area of future development. AI algorithms can assist in analyzing complex images and identifying patterns that may be difficult for human eyes to detect. By automating certain aspects of the imaging process, AI could reduce interpretation time and improve diagnostic accuracy, further enhancing patient care.
Conclusion
SPECT/CT scans have revolutionized patient care by combining the benefits of functional and anatomical imaging. The technology’s versatility makes it invaluable in oncology, cardiology, and neurology, where early and accurate diagnosis is essential for effective treatment. Although challenges such as radiation exposure and cost remain, advancements in technology and the potential integration with AI offer a promising future for SPECT/CT. As this imaging modality continues to evolve, it will undoubtedly play a pivotal role in shaping the future of diagnostic medicine, offering patients a higher standard of care and improving outcomes across various medical fields.
Kiranpet Nuclear Medicine & PET/CT Centre offers comprehensive medical imaging and diagnostic services, providing accurate and timely results to support patient care. Contact us today.