Have you ever wondered why your thyroid levels are abnormal even when your blood tests don’t give the full picture? A thyroid scan and uptake test help us understand not just the hormone levels in your blood, but how your thyroid gland is actually functioning inside your body.
If your doctor has suggested a thyroid scan in Bangalore, you might feel anxious about what the test involves, whether it is safe, or what the results will mean. We understand that concern, and in this blog, we will walk you through every step in the simplest way possible.
By the end of this guide, you will clearly understand why this test is done, how it works, and what your results truly indicate.
Medical Disclaimer:
This blog is intended for general informational and educational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. It is not a substitute for professional diagnosis, consultation, or treatment. Always consult your doctor or qualified healthcare provider regarding any medical condition and symptoms, or before undergoing a thyroid scan and uptake test. If you are pregnant, breastfeeding, or have existing health conditions, seek personalized medical guidance before proceeding with any diagnostic procedure.
Key Points at a Glance
- A thyroid scan and uptake is a nuclear medicine test.
- It uses a small, safe amount of radioactive iodine.
- It checks both the structure and function of the thyroid gland.
- It helps diagnose hyperthyroidism, hypothyroidism, Graves’ disease, nodules, and thyroiditis.
- The procedure usually takes place over 4–24 hours.
- Radiation exposure is minimal and considered safe.
- Preparation may include avoiding iodine-rich foods and certain medications.
- Results show whether uptake is high, normal, or low.
What Is A Thyroid Scan and Uptake?
A thyroid scan and uptake test is a nuclear medicine imaging procedure. It helps us see how well your thyroid gland absorbs iodine and how it is functioning.
Many people ask, “What is a thyroid uptake test?” Simply put, it measures how much iodine your thyroid absorbs from your bloodstream. Since iodine is essential for thyroid hormone production, this gives us valuable information about gland activity.
H2-Why Is Iodine Important for the Thyroid?
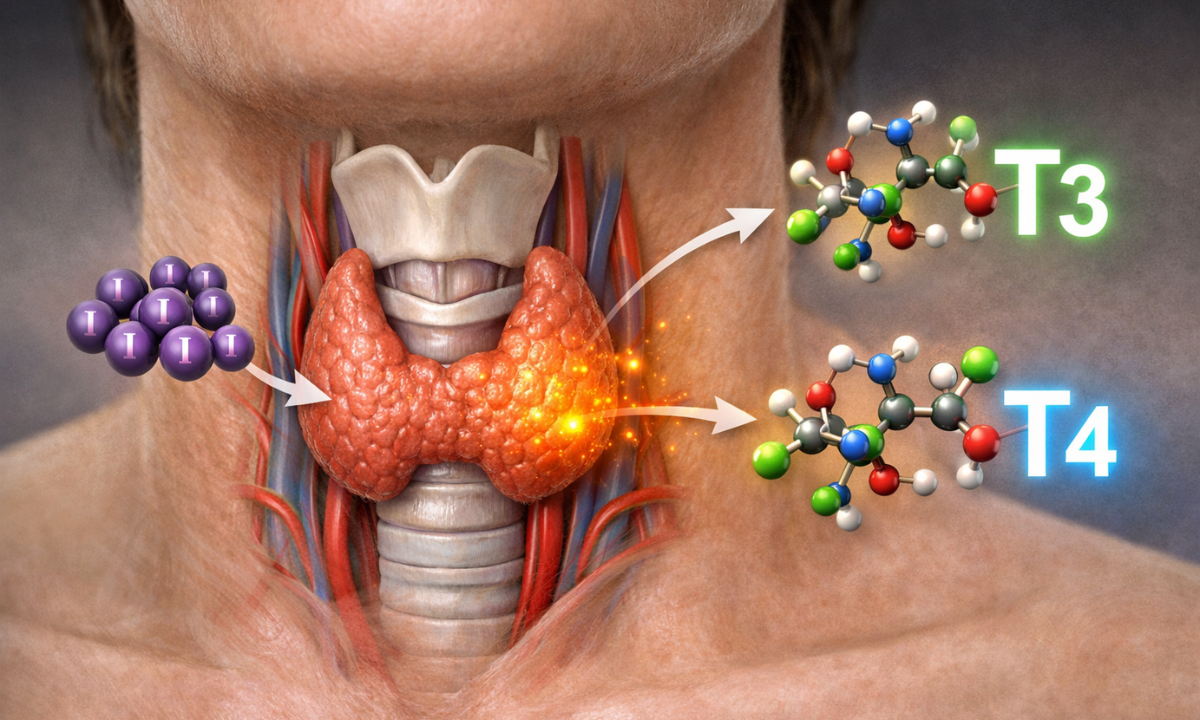
Iodine is a vital mineral that our body cannot produce on its own, which means we must obtain it through our diet. The thyroid gland depends entirely on iodine to produce hormones that regulate many essential body functions. Without adequate iodine, the thyroid cannot function properly, leading to a hormonal imbalance.
When we measure the thyroid uptake of iodine, we are essentially checking how efficiently the gland is using iodine to produce hormones.
Your thyroid gland uses iodine to make hormones called T3 and T4. These hormones control:
- Metabolism
- Heart rate
- Body temperature
- Energy levels
The thyroid uptake of iodine tells us whether your gland is overactive, underactive, or functioning normally.
What Is the Purpose of a Thyroid Uptake Scan?
Many patients ask, “What is the purpose of a thyroid uptake scan?” Let us break it down clearly.
This test helps us understand not just how much hormone is present in the blood, but how actively the thyroid gland is working. It gives functional information that other imaging tests cannot provide.
The main purposes include:
| Purpose | What It Helps Detect |
|---|---|
| Measure thyroid function | Hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism |
| Evaluate nodules | Hot or cold nodules |
| Diagnose diseases | Graves’ disease, thyroiditis |
| Cancer follow-up | Check for spread or residual tissue |
This test gives more detailed information than blood tests alone.
Conditions Diagnosed by Thyroid Scan and Uptake
Here are the most common conditions identified:
1. Hyperthyroidism
- High iodine uptake – This means the thyroid is absorbing more iodine than normal, indicating excessive hormone production.
- The thyroid is overactive – The gland produces too much T3 and T4 hormones, speeding up body functions.
- Common in Graves’ disease – In this autoimmune condition, the entire gland becomes uniformly overactive.
2. Hypothyroidism
- Low iodine uptake – The thyroid absorbs very little iodine, suggesting reduced hormone production.
- The thyroid is underactive – This leads to slower metabolism, fatigue, weight gain, and cold intolerance.
3. Graves’ Disease
- Diffuse, high uptake throughout the gland – The scan shows uniform increased activity across the thyroid, which is a classic sign of this autoimmune disorder.
4. Thyroid Nodules
- “Hot” nodules (usually non-cancerous) – These are overactive areas that absorb more iodine and rarely indicate cancer.
- “Cold” nodules (require further evaluation) – These areas absorb less iodine and may need additional tests, such as biopsy, to rule out malignancy.
What Are The Types of Tracers Used
In a thyroid scan and uptake procedure, we use very small and safe amounts of radioactive material called tracers. These tracers help us visualize how the thyroid gland absorbs iodine and how actively it is functioning.
The amount used is carefully calculated and is considered safe for diagnostic purposes.
Different tracers may be selected depending on whether the goal is to measure iodine uptake or to obtain detailed thyroid images.
The test uses small amounts of radioactive material. These include:
| Tracer | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Radioactive iodine (I-123 or I-131) | Measures uptake |
| Technetium-99m | Used in tc 99m thyroid scan |
The radioactive iodine uptake test is the most commonly performed method.
How to Prepare for Thyroid Scan and Uptake
Preparation is very important for accurate results. The thyroid gland is highly sensitive to iodine levels in the body, and even small dietary or medication changes can influence the test outcome.
Proper preparation ensures that the thyroid uptake measurement truly reflects your gland’s natural function.
We always recommend carefully following your doctor’s instructions a few days before the test. This helps avoid false readings and reduces the need for repeat testing.
Foods to Avoid Before Thyroid Uptake Scan
Many patients ask about foods to avoid before a thyroid uptake scan. Since iodine intake can interfere with results, you may be asked to avoid iodine-rich foods for a few days before the test:
- Seafood
- Iodized salt
- Dairy products
- Seaweed
- Multivitamins containing iodine
Medication Guidelines
Certain medications can also affect iodine absorption and thyroid function. Your doctor may advise temporarily stopping specific drugs before the scan.
Your doctor may advise stopping:
- Thyroid medications
- Certain cough syrups
- Iodine supplements
Always follow medical advice carefully.
Is the Test Safe?
Yes, it is very safe. The radiation exposure is minimal and comparable to a standard X-ray.
However:
- It is not recommended during pregnancy.
- Breastfeeding mothers may need special instructions.
Step-by-Step Procedure of Thyroid Scan and Uptake
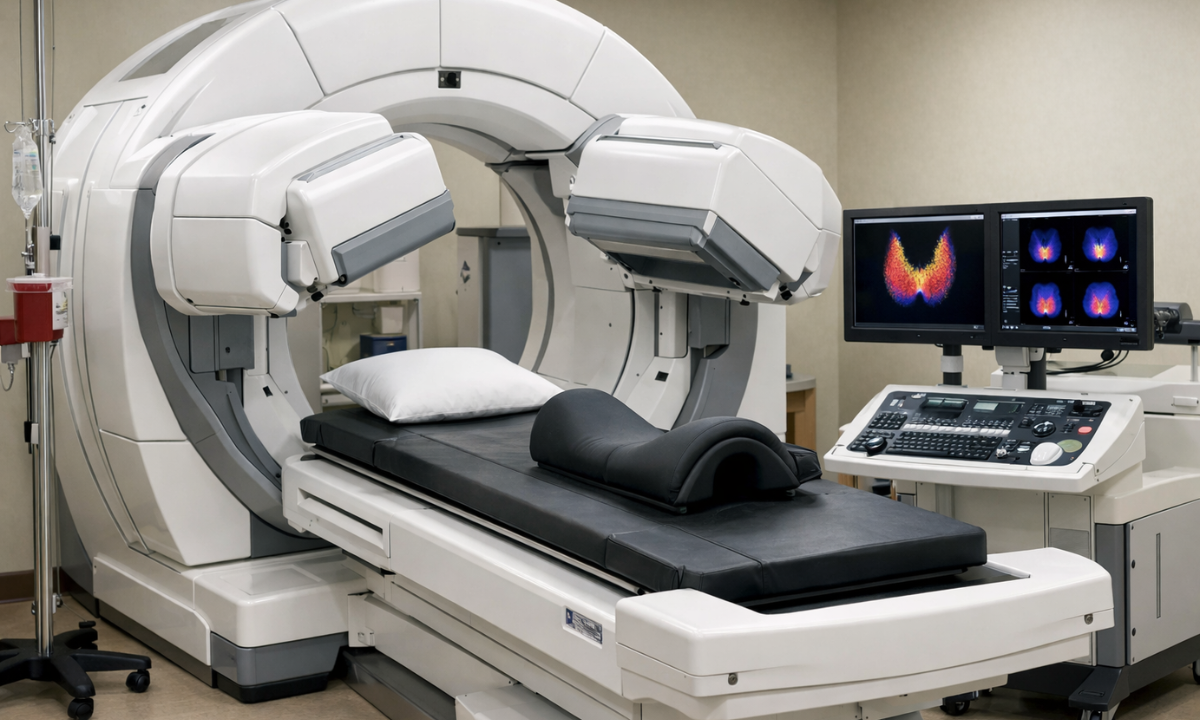
Let us walk you through the entire process so you feel comfortable. Knowing what to expect can reduce anxiety and help you prepare mentally for the test. The procedure is simple, painless, and performed on an outpatient basis in most cases.
Step 1: Administration
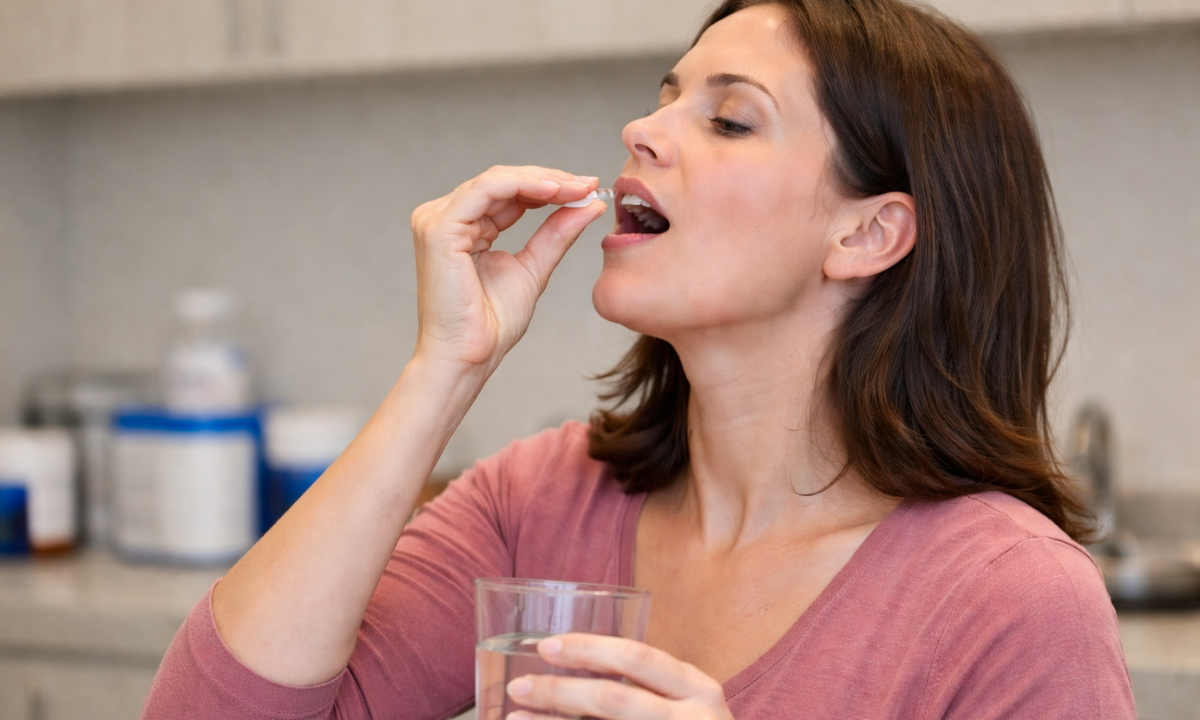

You swallow a small capsule or liquid containing radioactive iodine. It is tasteless and painless.
The dose is very small and carefully measured according to safety guidelines. After taking the capsule, you can usually leave the department and return later for the scan, unless instructed otherwise.
Step 2: Waiting Period

- 4–6 hours after ingestion
- Sometimes an additional 24-hour measurement
This waiting period allows the radioactive iodine to travel through your bloodstream and accumulate in the thyroid gland. The thyroid naturally absorbs iodine, so this step is essential for accurate results.
In some cases, doctors measure uptake twice, once at 4–6 hours and again at 24 hours, to compare early and delayed absorption patterns.
Step 3: Thyroid Uptake Measurement
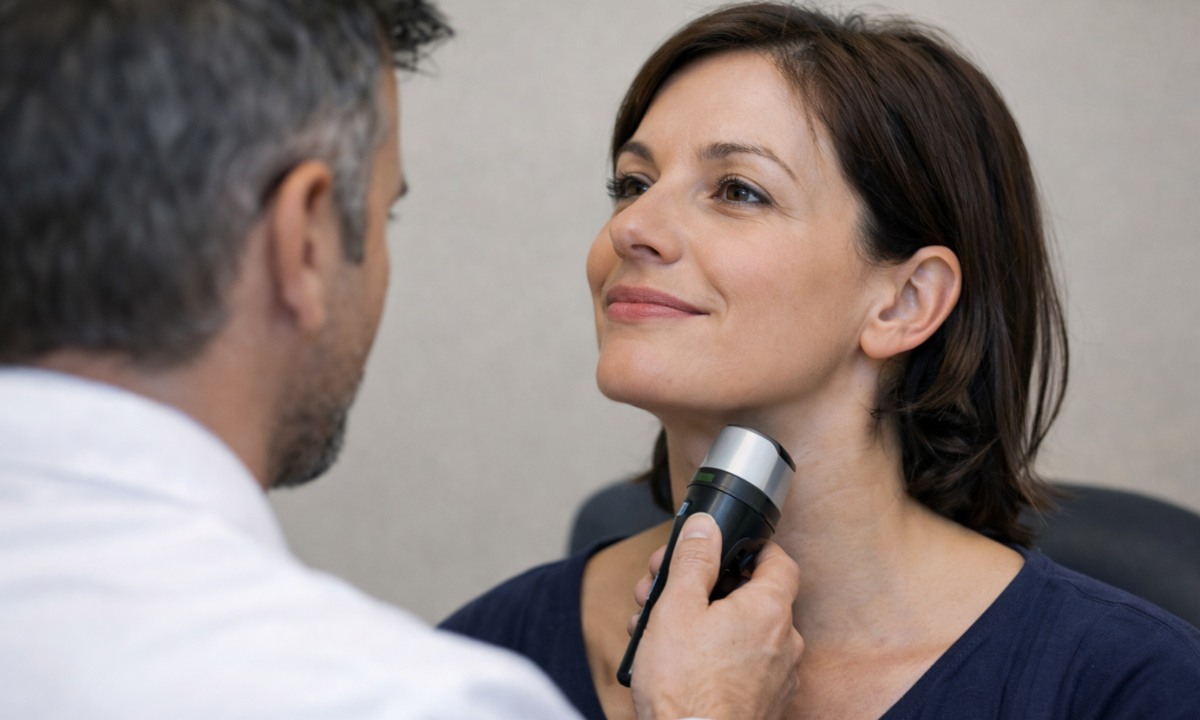
A small probe is placed near your neck. It measures the percentage of iodine absorbed. This is called thyroid uptake measurement.
The probe does not touch your skin and does not cause discomfort. It simply detects the radiation emitted from the iodine inside your thyroid and calculates how much has been absorbed.
Step 4: Thyroid Scan Imaging
You lie on a table while a gamma camera takes images. The scanning part usually takes 20–30 minutes.
During the scan, you will be asked to remain still so that clear images can be obtained. The camera does not touch you and does not cause pain. It captures detailed pictures of the thyroid’s size, shape, and activity distribution, helping doctors identify hot or cold nodules and overall gland function.
How Long Does the Entire Test Take?
One of the most common concerns we hear is about the total time required for a thyroid scan and uptake test. While the actual scanning process is short, the overall procedure is spread out because the thyroid needs time to absorb the radioactive iodine properly.
Most of the waiting time happens between taking the capsule and the imaging session. The good news is that the active parts of the test are quick, simple, and completely painless.
| Phase | Duration |
|---|---|
| Capsule intake | 5 minutes |
| Waiting time | 4–24 hours |
| Uptake measurement | 10 minutes |
| Imaging | 30 minutes |
The imaging itself is quick and painless.
Understanding Thyroid Uptake Test Results
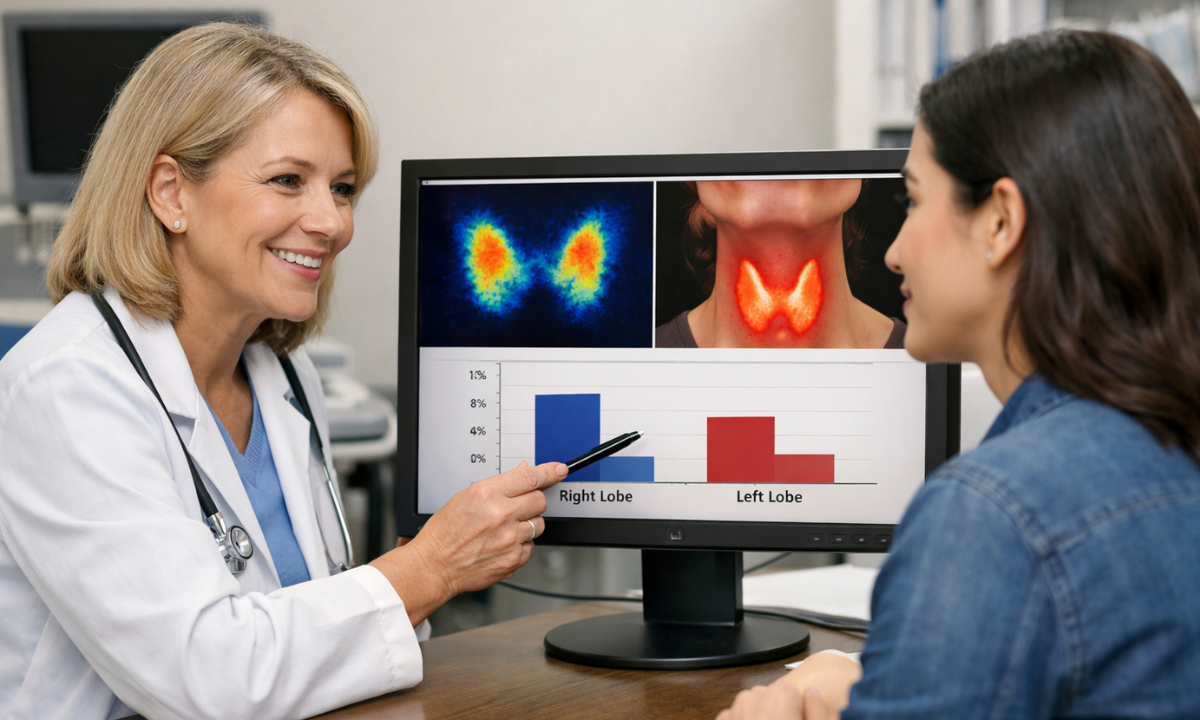
Once the scan is completed, your doctor will carefully analyze both the images and the percentage of iodine absorbed by your thyroid gland. The results are interpreted along with your symptoms, blood test reports, and clinical history. This combined approach gives a complete picture of your thyroid health.
The uptake percentage usually falls within a reference range provided by the laboratory. Values that are too high or too low help doctors identify specific thyroid disorders.
Normal Results
In a normal thyroid scan and uptake study, the gland appears balanced in size, shape, and activity. The iodine distribution is uniform, meaning the entire gland is functioning evenly.
| Parameter | Normal Finding |
|---|---|
| Size | Normal size |
| Shape | Symmetrical |
| Uptake | Even distribution |
A normal result usually suggests that thyroid hormone production is appropriate and well-regulated.
High Uptake
High uptake means the thyroid is absorbing more iodine than expected. This typically indicates that the gland is overactive and producing excess hormones.
Indicates:
- Hyperthyroidism
- Graves’ disease
The gland appears darker on imaging due to increased tracer concentration. Patients with high uptake may experience symptoms such as weight loss, palpitations, anxiety, heat intolerance, and excessive sweating.
Low Uptake
Low uptake means the thyroid is absorbing very little iodine. This suggests reduced thyroid activity or inflammation affecting the gland.
Indicates:
- Hypothyroidism
- Thyroiditis
- Inflammation
Patients with low uptake may report fatigue, weight gain, depression, cold intolerance, or sluggishness. In some cases, temporary inflammation of the gland (thyroiditis) can also cause reduced iodine absorption.
Hot vs Cold Nodules
Sometimes, the scan reveals specific areas within the thyroid that function differently from the surrounding tissue. These are called nodules.
| Nodule Type | Meaning | Cancer Risk |
|---|---|---|
| Hot Nodule | Overactive area | Rarely cancerous |
| Cold Nodule | Less active area | Needs further evaluation |
A hot nodule absorbs more iodine and appears darker on the scan. These nodules are usually benign and may cause hyperthyroidism.
A cold nodule absorbs less iodine and appears lighter. While many cold nodules are harmless, they require further evaluation, such as ultrasound or biopsy, to rule out malignancy.
Understanding your thyroid uptake test results helps determine the next treatment step. Whether it involves medication, radioactive iodine therapy, monitoring, or further imaging through a PET scan in Bangalore.
Thyroid Scan and Uptake vs SPECT Scan
Many patients wonder whether a thyroid scan and uptake test is the same as an SPECT scan. While both are nuclear medicine imaging techniques and may use similar tracers, their imaging capability and level of detail can differ. A SPECT scan in Bangalore can also be used for thyroid evaluation, especially when more precise localization or 3D imaging is required.
| Feature | Thyroid Scan & Uptake | SPECT Scan |
|---|---|---|
| Imaging Type | Functional imaging (2D planar imaging) | 3D functional imaging |
| Main Purpose | Measure iodine uptake and assess thyroid function | Detailed localization and enhanced anatomical correlation |
| Tracer Used | Radioactive iodine (I-123/I-131) or Tc-99m | Tc-99m or other gamma-emitting tracers |
| Detail Level | Evaluates function and nodules | Provides more precise 3D images |
| Other Uses | Primarily thyroid evaluation | Thyroid, heart, brain, bone, and other organs |
Both tests are safe and effective, and your doctor will choose the most appropriate one based on your symptoms and diagnostic needs.
When Do Doctors Recommend This Test?
Doctors usually recommend a thyroid scan and uptake test when blood reports alone do not fully explain your symptoms.
While thyroid function tests (TSH, T3, T4) show hormone levels, they do not always reveal how actively the gland is functioning or whether a specific area of the thyroid is abnormal. This imaging test helps identify the exact cause of imbalance and guides the right treatment plan.
You may be advised to take this test if:
- Blood tests show abnormal thyroid levels
If your TSH, T3, or T4 levels are too high or too low, this test helps determine whether the gland itself is overactive, underactive, or inflamed. - You have thyroid swelling
Visible enlargement in the neck, also called goitre, may require imaging to assess size, symmetry, and functional activity. - You have unexplained weight changes
Sudden weight loss or gain without lifestyle changes may indicate thyroid dysfunction, which this scan can clarify. - Nodules are detected on ultrasound
If an ultrasound shows thyroid nodules, the uptake scan helps identify whether they are “hot” (functioning) or “cold” (non-functioning). - Hyperthyroidism symptoms are present
Symptoms such as rapid heartbeat, tremors, excessive sweating, anxiety, or heat intolerance often require a radioactive iodine uptake test to confirm the diagnosis.
In some cases, the test is also recommended after thyroid surgery or during follow-up for thyroid cancer to evaluate remaining thyroid tissue.
If you are considering a thyroid Scan in Bangalore, choosing an experienced diagnostic centre ensures accurate reporting, advanced imaging technology, and patient safety throughout the procedure.
When is a Tc 99m Thyroid Scan Preferred?
A tc 99m thyroid scan is often chosen when:
- Quick imaging is required
- Uptake measurement is less critical
- Structural assessment is the main focus
It uses technetium-99m instead of iodine.
Tips for a Smooth Experience
Here are some simple tips to follow before the scan for a comfortable experience:
- Wear comfortable clothing
- Remove neck jewellery
- Inform your doctor about medications
- Stay hydrated
- Follow dietary restrictions strictly
Preparation ensures reliable results.
Final Thoughts
A thyroid scan and uptake test give us a clear picture of how your thyroid gland is functioning, beyond what blood tests can reveal. It helps diagnose conditions early, guide treatment, and monitor recovery safely.
If you are planning a thyroid scan in Bangalore, choosing a trusted centre like our Kiran PET CT ensures accurate imaging, advanced technology, and compassionate care under expert supervision.
Understanding your thyroid health today can prevent bigger problems tomorrow, and that is why this simple yet powerful test truly matters.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the purpose of a thyroid uptake scan?
The purpose of a thyroid uptake scan is to measure how much iodine your thyroid gland absorbs and how actively it produces hormones. It helps diagnose conditions such as hyperthyroidism, hypothyroidism, Graves’ disease, and thyroiditis.
The test also identifies whether nodules are overactive or underactive, guiding accurate treatment decisions.
2. What is the difference between a thyroid scan and a thyroid uptake?
A thyroid uptake measures the percentage of radioactive iodine absorbed by the thyroid gland, showing how well it functions.
A thyroid scan, on the other hand, creates images of the gland to evaluate its size, shape, and activity pattern. Together, they provide both functional measurement and visual assessment.
3. What is a normal uptake for a thyroid scan?
Normal thyroid uptake values vary slightly by laboratory, but typically range between 10% and 30% at 24 hours after iodine intake.
A normal result indicates balanced thyroid hormone production and even tracer distribution throughout the gland. Values above or below this range may suggest overactive or underactive thyroid conditions.
4. Which scan is best for the thyroid?
The best scan depends on the clinical concern.
- A thyroid scan and uptake test are ideal for evaluating thyroid function and hyperthyroidism.
- Ultrasound is best for assessing nodules and structures.
- In cancer evaluation, PET or SPECT scans may be recommended.
Your doctor selects the most appropriate test based on symptoms and diagnosis needs.
5. Does the test hurt?
No, the test is completely painless and non-invasive. You only need to swallow a small capsule or liquid, and the rest of the procedure involves external scanning with a gamma camera.
There are no injections in most cases, no cuts, and no discomfort. Patients simply lie still while images are captured.
6. Can children undergo this test?
Yes, children can undergo a thyroid scan and uptake test if it is medically necessary. The radioactive dose is adjusted according to body weight to ensure safety.
It is performed only when clearly indicated and under specialist supervision. Parents are given specific instructions to ensure comfort and safety throughout the procedure.
Reference:
1. From Google
2. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diagnostics/thyroid-uptake-scan