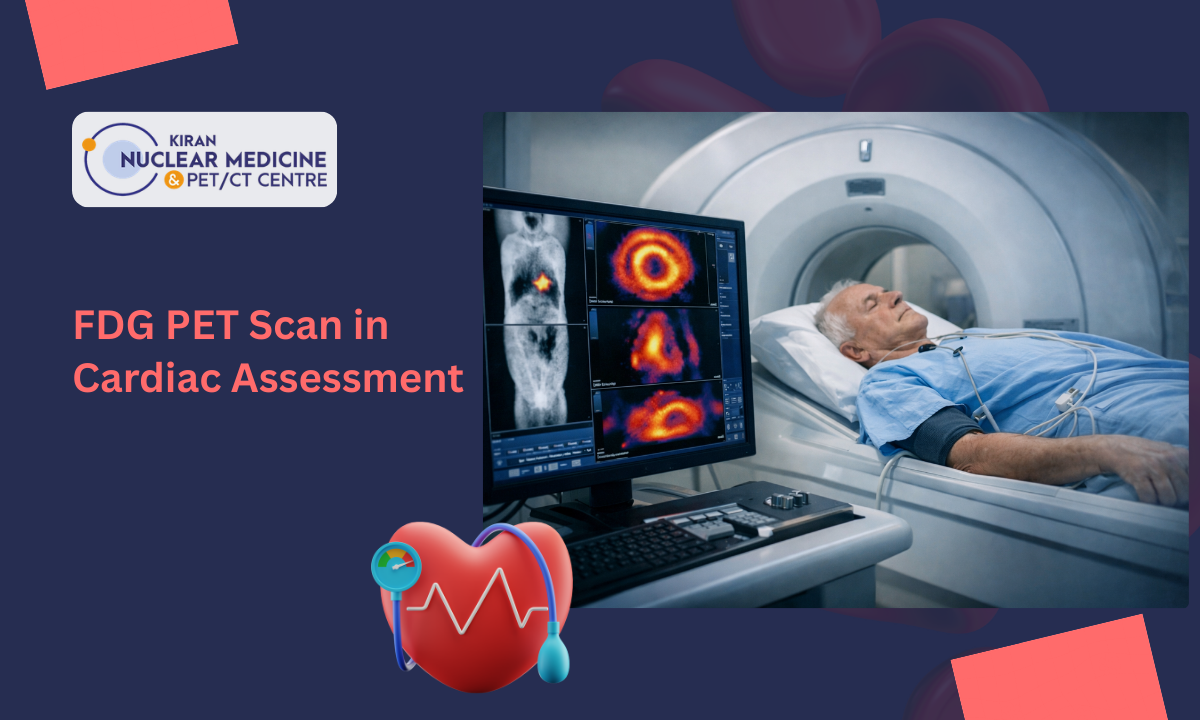
As a doctor at Kiran PET, I often meet patients who are confused, anxious, and searching for clear answers about their heart health. Many have been told they need an FDG PET Scan for a detailed cardiac assessment, but they don’t fully understand why.
In this blog, I’ll walk you through everything, from what a cardiac assessment is to how FDG positron emission tomography works, when we recommend an 18 FDG PET scan, and how it plays a critical role in diagnosing complex heart conditions.
I’ll also explain why choosing the right PET scan centre in Bangalore matters for accurate results. Let’s begin.
Understanding Cardiac Assessment
Before we dive into imaging, we must understand what a cardiac assessment is.
A cardiac assessment is a comprehensive evaluation of the heart’s structure, function, blood supply, and tissue health. It helps us determine:
- How well your heart muscle is working
- Whether blood flow is adequate
- If there are damaged or scarred areas
- Whether inflammation or infection is present
- If the heart muscle is still viable after a heart attack
Traditional tests like ECG and stress tests provide useful information. However, when we need deeper insights at the cellular level, we rely on advanced imaging like the FDG PET Scan.
What is an FDG PET Scan?
An FDG PET Scan is a highly advanced imaging technique that shows how tissues in the body metabolise glucose.
FDG (Fluorodeoxyglucose) is a radioactive glucose analogue. Since heart muscle cells use glucose for energy, especially when damaged, FDG helps us visualise metabolic activity.
FDG positron emission tomography is a nuclear imaging technique where:
- FDG is injected into the bloodstream
- It travels to metabolically active tissues
- The PET scanner detects radiation signals
- A 3D image of metabolic activity is generated
In cardiology, this allows us to see whether heart muscle cells are alive, inflamed, infected, or scarred.
Why the FDG PET Scan is Crucial in Cardiac Assessment
An FDG PET scan helps evaluate heart muscle viability by identifying areas with reduced blood flow but still living tissue.
It is especially useful in assessing conditions like coronary artery disease and determining the need for revascularisation procedures.
By providing detailed metabolic information, it supports accurate diagnosis and better treatment planning in cardiac patients. In my clinical experience, the FDG PET Scan is transformative in cardiac assessment for several reasons.
1. Detecting Viable Myocardium
After a heart attack, parts of the heart muscle may stop functioning. But not all non-functioning areas are dead.
FDG PET helps us determine:
- Is the muscle permanently scarred?
- Or is it “hibernating” and recoverable?
If viable tissue is present, procedures like angioplasty or bypass surgery can restore function.
2. Diagnosing Cardiac Sarcoidosis
Cardiac sarcoidosis is an inflammatory condition affecting the heart. It’s difficult to diagnose using conventional imaging.
An 18 FDG PET scan highlights areas of inflammation, helping us:
- Confirm diagnosis
- Monitor treatment
- Adjust medications
3. Evaluating Myocarditis
Myocarditis (heart muscle inflammation) can cause unexplained heart failure, chest pain, or arrhythmias. FDG PET detects areas of active inflammation by highlighting increased metabolic activity in affected heart tissues, even when routine tests like ECG or echocardiography appear normal.
This makes it particularly valuable in early diagnosis, assessing the severity of inflammation, and monitoring response to treatment over time.
4. Detecting Prosthetic Valve Infections
In suspected infective endocarditis, especially in patients with prosthetic heart valves, FDG PET is extremely useful in identifying infection around the valve site. It can detect abnormal metabolic activity caused by infection that may not be clearly visible on standard imaging techniques.
Early and accurate detection helps guide timely antibiotic therapy or surgical intervention, reducing the risk of serious complications.
The Science Behind 18 FDG PET Scan
The 18 FDG PET scan uses Fluorine-18, a radioactive tracer with a short half-life. This ensures:
- Minimal radiation exposure
- High-quality imaging
- Safe outpatient procedure
Preparation is crucial. For cardiac assessment, we often modify the patient’s diet before scanning to suppress normal heart glucose uptake and highlight abnormal areas.
This level of precision makes FDG PET superior to many traditional imaging techniques.
Role of FDG PET Scan in Different Heart Conditions
The FDG PET scan plays an important role in diagnosing and managing a wide range of cardiac conditions. Unlike routine imaging tests that mainly show structural changes, FDG PET provides metabolic information, helping doctors understand how the heart muscle is functioning at a cellular level.
This advanced insight allows for more accurate diagnosis, better risk assessment, and personalised treatment planning in complex cardiac cases.
- Heart Failure: In patients with severe heart failure, we must decide whether revascularisation will help. FDG PET determines myocardial viability, guiding life-saving decisions.
- Ischaemic Heart Disease: It shows areas with reduced blood flow and metabolism mismatch.
- Inflammatory Heart Disease: FDG PET detects inflammation before structural damage becomes visible.
- Post-Surgery Monitoring: After cardiac procedures, we use FDG PET to monitor healing and detect complications early.
FDG PET Scan in Bangalore: Why Advanced Imaging Matters
As cardiac cases grow more complex, having access to high-quality imaging is essential. When patients search for an FDG PET scan in Bangalore, they are often looking for:
- Experienced nuclear medicine specialists
- Advanced PET-CT equipment
- Accurate reporting
- Clinical integration with cardiology teams
At KiranPET, we combine technology with clinical expertise. Accurate cardiac assessment isn’t just about imaging — it’s about interpretation and personalised care.
What is a Grid of Tests Before FDG PET?
Before recommending an FDG PET scan, a thorough clinical evaluation is essential. FDG PET is an advanced and specialised imaging test, so we first rely on standard cardiac investigations to understand the patient’s symptoms, structural heart condition, and biochemical markers.
This stepwise approach ensures that the scan is used appropriately and only when it can provide additional, decision-changing information.
Before recommending an FDG PET Scan, I usually evaluate:
- ECG
- Echocardiogram
- Blood markers
- Stress test result
- MRI (if needed)
FDG PET is typically recommended when:
- Diagnosis is unclear
- Viability assessment is required
- Inflammation is suspected
- Previous tests show inconclusive results
Safety and Preparation for Cardiac FDG PET
Patients often ask if the scan is safe.
The answer is yes.
Preparation Includes:
- Low-carb, high-fat diet 24 hours prior – This helps suppress normal heart muscle glucose uptake, allowing clearer detection of abnormal metabolic activity.
- Fasting for 6 hours – Fasting ensures stable glucose levels and improves the accuracy of FDG uptake in targeted areas.
- Blood sugar control – Maintaining optimal blood glucose levels is essential for reliable imaging results.
- Medication adjustments – Certain medications may need temporary modification to avoid interference with scan accuracy.
The scan typically takes 1–2 hours.
Radiation exposure is controlled and within safe medical limits.
Choosing the Right PET Scan Centre in Bangalore
When selecting a PET scan centre in Bangalore, consider:
- Accreditation and certifications
- Advanced PET-CT technology
- Experienced nuclear medicine physicians
- Collaboration with cardiologists
- Proper patient preparation protocols
A high-quality cardiac assessment depends on precision imaging and expert interpretation.
Limitations of the FDG PET Scan
While powerful, the FDG PET scan does have certain limitations that both doctors and patients should be aware of. It is a highly sensitive imaging modality, but its accuracy depends heavily on proper patient selection and preparation.
- Requires strict preparation – The scan demands dietary modification and fasting before the procedure. If preparation guidelines are not followed correctly, the results may be suboptimal or difficult to interpret.
- Not ideal for unstable patients – Patients who are haemodynamically unstable or critically ill may not be suitable candidates, as the scan requires time, monitoring, and the ability to lie still during imaging.
- Can be affected by uncontrolled diabetes – High blood sugar levels interfere with FDG uptake, potentially reducing image clarity and diagnostic reliability. Proper glucose control is essential before performing the scan.
Additionally, FDG PET may not be readily available in all centres and can be relatively expensive compared to routine cardiac imaging tests.
However, in appropriate cases, its diagnostic accuracy is unmatched, particularly when assessing myocardial viability, inflammation, and complex cardiac conditions.
Future of FDG PET in Cardiac Assessment
Cardiac imaging is evolving rapidly. Hybrid PET-MRI systems and advanced tracers are improving sensitivity and specificity.
In the future, FDG PET will:
- Help personalise heart failure treatment
- Predict arrhythmia risk
- Detect early inflammatory heart disease
- Guide immunosuppressive therapy
The role of FDG PET Scan in cardiac assessment will only expand.
Final Thoughts
As a physician at Kiran PET, I firmly believe that the FDG PET Scan has transformed modern cardiac assessment. It allows us to look beyond structure and understand the heart at a metabolic level.
Whether evaluating viability after a heart attack, diagnosing cardiac sarcoidosis, or investigating unexplained heart failure, FDG PET provides answers that other tests cannot.
If you are considering an FDG PET scan in Bangalore, ensure you choose a trusted and technologically advanced PET scan centre in Bangalore. The accuracy of your diagnosis, and ultimately your treatment outcome, depends on it.
Early diagnosis saves the heart muscle. And saving heart muscle saves lives.
FAQs
1. What is a Cardiac Assessment?
A cardiac assessment is a comprehensive evaluation of the heart’s structure and function. It includes tests such as ECG, echocardiography, blood investigations, stress testing, and advanced imaging when required. The goal is to assess blood flow, pumping efficiency, electrical activity, and tissue health to diagnose heart disease accurately and guide appropriate treatment planning.
2. What is an FDG PET Scan?
An FDG PET scan is an advanced nuclear imaging test that uses a small amount of radioactive glucose (FDG) to evaluate metabolic activity in heart tissues. Since active or inflamed cells consume more glucose, the scan helps detect viable heart muscle, inflammation, or infection that may not be visible on routine imaging.
3. What is the Role of the FDG PET Scan in Cardiac Assessment?
FDG PET plays a crucial role in identifying viable but weakened heart muscle, detecting inflammation such as myocarditis, and diagnosing infections like prosthetic valve endocarditis. It provides metabolic insights beyond structural imaging, helping cardiologists make informed decisions about revascularisation, medical therapy, or surgical intervention in complex cases.
4. Is an 18 FDG PET Scan Safe?
Yes, the 18 FDG PET scan is considered safe when performed under medical supervision. It uses a controlled amount of radioactive tracer, and radiation exposure remains within accepted medical safety limits. Proper preparation and expert monitoring further ensure patient safety and accurate diagnostic outcomes.
5. How Long Does the Procedure take at KiranPET?
The procedure typically takes about 1–2 hours, including preparation time and scanning. After tracer injection, there is a waiting period to allow proper distribution in the body before imaging begins. The actual scan is painless, and patients can usually resume normal activities shortly afterwards.
6. How Should I Prepare for a Cardiac FDG PET Scan?
Preparation involves following a low-carbohydrate, high-fat diet 24 hours before the scan, fasting for at least 6 hours, and maintaining proper blood sugar control. Certain medications may require adjustment. Proper preparation is essential to ensure accurate imaging and reliable diagnostic results.
7. When is an FDG PET Scan Recommended?
An FDG PET scan is recommended when conventional cardiac tests provide inconclusive results or when assessing myocardial viability before revascularisation. It is also advised in suspected inflammatory heart diseases, prosthetic valve infections, or complex cardiac conditions where metabolic evaluation is necessary for accurate diagnosis and treatment planning.